When you're stressed, your body produces a distinctive type of sweat that often smells different from regular exercise-induced perspiration. This phenomenon, commonly known as stress sweat, is closely linked to your body's production of cortisol and other stress hormones. Understanding the science behind stress sweat can help you better manage its effects and reduce any associated anxiety about body odor.
The Science Behind Stress Sweat
Stress sweat is fundamentally different from regular sweat because it's produced by different glands and contains unique chemical compounds. While regular sweat is primarily composed of water and electrolytes, stress sweat contains additional proteins and lipids that interact with bacteria on your skin, creating a more pungent odor.
Different Types of Sweat Glands and Their Role
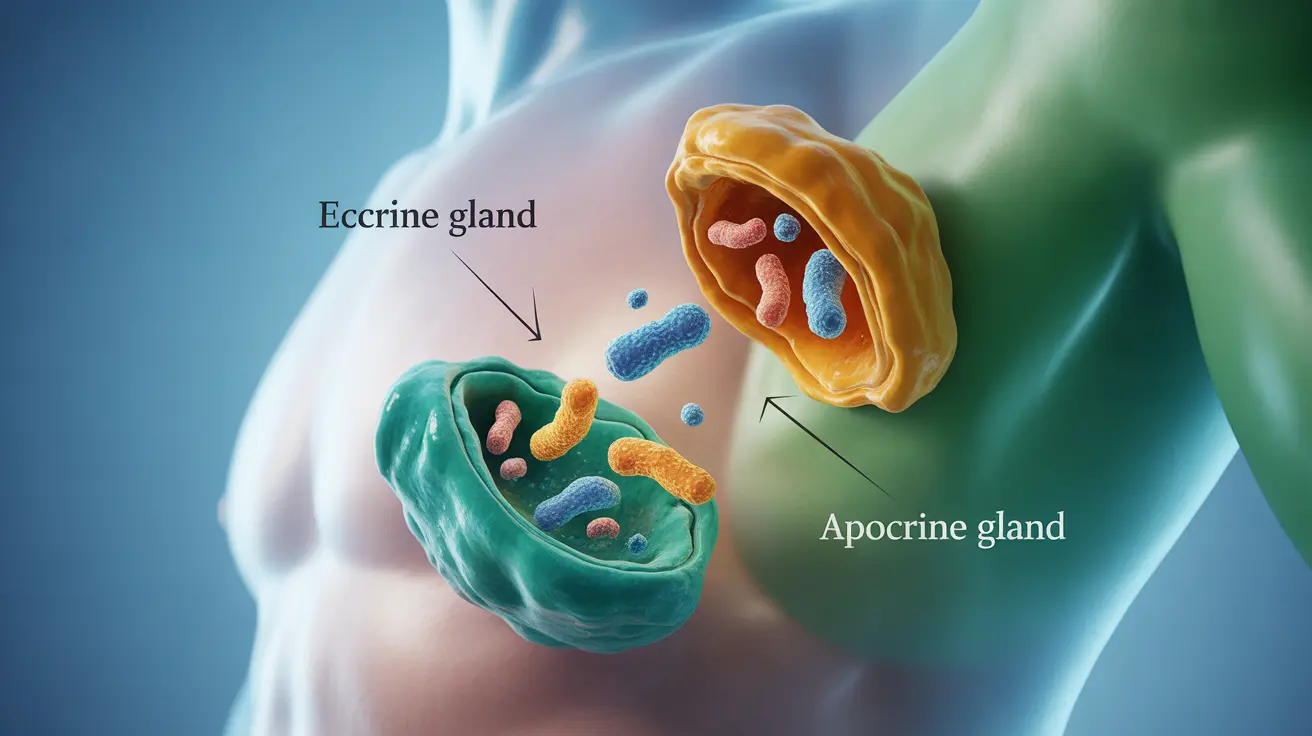
Your body has two main types of sweat glands that contribute to body odor:
- Eccrine glands: Produce regular, water-based sweat
- Apocrine glands: Produce stress sweat, concentrated in areas like armpits and groin
The apocrine glands are primarily responsible for stress-related body odor. These glands become active during puberty and respond specifically to emotional stimuli like anxiety, fear, and stress.
The Chemical Composition of Stress Sweat
Stress sweat has a distinct chemical makeup that sets it apart from regular perspiration. When cortisol levels rise, your body releases a mixture of substances including:
- Proteins
- Fatty acids
- Steroids
- Sulfur compounds
These components, when broken down by bacteria on your skin, create the characteristic sharp, acidic smell associated with stress sweat.
Managing Stress Sweat and Its Odor
Hygiene Practices
To effectively manage stress sweat odor, consider these strategies:
- Use antibacterial soap when showering
- Apply antiperspirant in the evening
- Wear breathable, natural fabrics
- Change clothes promptly after stressful situations
Stress Management Techniques
Reducing stress can help minimize stress sweat production:
- Practice regular meditation
- Engage in deep breathing exercises
- Maintain regular physical activity
- Get adequate sleep
- Consider stress-reduction therapy
Frequently Asked Questions
What does cortisol smell like and does it cause stress sweat odor? Cortisol itself doesn't have a smell, but it triggers the production of stress sweat, which has a distinct sharp, acidic odor when broken down by bacteria on the skin.
Why does stress sweat smell different and stronger than regular sweat? Stress sweat contains different chemical compounds, including proteins and lipids, that when broken down by bacteria create a more pungent odor compared to regular exercise-induced sweat.
Which sweat glands are responsible for the smell associated with stress sweat? The apocrine glands, located primarily in the armpits and groin area, are responsible for producing stress sweat and its associated odor.
How can I reduce or manage the strong odor caused by stress sweat? You can manage stress sweat odor through proper hygiene, using antiperspirants, wearing breathable clothing, and practicing stress management techniques like meditation and regular exercise.
What chemicals in stress sweat cause its characteristic pungent odor? The combination of proteins, fatty acids, steroids, and sulfur compounds in stress sweat, when broken down by skin bacteria, creates its characteristic pungent smell.