Dihydrotestosterone (DHT) plays a crucial role in human development and health, particularly in males. This powerful androgen hormone, derived from testosterone, influences various aspects of physical development, from early fetal growth to adult characteristics. Understanding DHT's function and effects is essential for comprehending both its necessary biological roles and potential health concerns.
While DHT is vital for normal development, it can also contribute to certain health conditions, most notably male pattern baldness. This comprehensive guide explores the nature of DHT, its formation in the body, and its various effects on health and development.
The Formation and Function of DHT
DHT is created through a complex biological process where the enzyme 5-alpha reductase converts testosterone into dihydrotestosterone. This conversion happens in various tissues throughout the body, including the prostate, skin, and hair follicles. The resulting hormone is significantly more potent than testosterone, binding more strongly to androgen receptors in the body's tissues.
During fetal development, DHT is crucial for the formation of male external genitalia and plays a vital role in the development of male secondary sexual characteristics during puberty. These include facial hair growth, voice deepening, and muscle development.
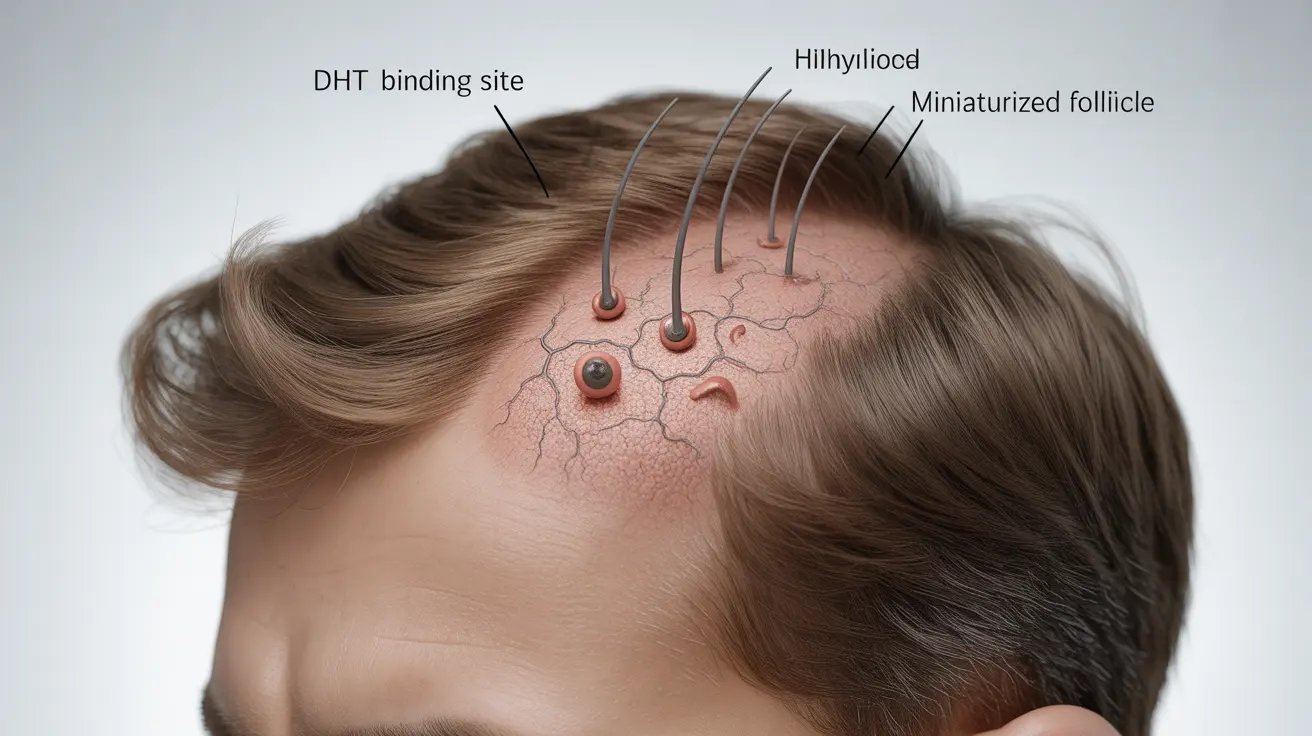
DHT's Role in Hair Growth and Loss
One of DHT's most notable effects is its influence on hair growth patterns. In individuals with genetic sensitivity, DHT can bind to receptors in scalp hair follicles, leading to their gradual miniaturization. This process results in progressively thinner hair and eventually leads to male pattern baldness, also known as androgenetic alopecia.
The Hair Loss Connection
Not everyone is equally susceptible to DHT-related hair loss. The condition depends largely on genetic factors that determine how sensitive hair follicles are to DHT. While the hormone promotes body and facial hair growth, it paradoxically contributes to scalp hair loss in susceptible individuals.
Health Implications of DHT Levels
Maintaining appropriate DHT levels is crucial for overall health. Both excessive and insufficient levels can lead to various health concerns:
High DHT Levels
- Increased risk of prostate enlargement
- Accelerated male pattern baldness
- Acne
- Excessive body hair growth
Low DHT Levels
- Delayed or incomplete male sexual development
- Reduced muscle mass
- Decreased body and facial hair
- Potential fertility issues
Treatment Approaches and Management
Several treatment options exist for managing DHT-related conditions, particularly for those dealing with hair loss or prostate issues. These include FDA-approved medications that work by blocking DHT production or its effects on target tissues.
Natural approaches to DHT management may include dietary changes, herbal supplements, and lifestyle modifications, though their effectiveness varies and should be discussed with healthcare providers.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is dihydrotestosterone (DHT) and how is it formed in the body?
DHT is a hormone derived from testosterone through the action of the enzyme 5-alpha reductase. It's formed in various tissues throughout the body and is more potent than testosterone in its effects on androgen receptors.
How does DHT affect hair growth and contribute to hair loss?
DHT can bind to receptors in scalp hair follicles, causing them to shrink in genetically susceptible individuals. This leads to progressively thinner hair and eventual hair loss, particularly in male pattern baldness.
What are the health risks associated with having high or low levels of DHT?
High DHT levels can lead to prostate enlargement, accelerated hair loss, and acne. Low levels may result in incomplete male sexual development, reduced muscle mass, and potential fertility issues.
What treatments and natural remedies are available to block or reduce DHT for hair loss?
Treatment options include FDA-approved medications that block DHT production or activity, along with natural approaches such as dietary modifications and herbal supplements. Medical supervision is recommended for any treatment plan.
How does DHT differ from testosterone in its effects on male development and health?
While both are androgens, DHT is more potent than testosterone and plays specific roles in male sexual development and maturation. DHT is particularly crucial during fetal development and puberty, affecting external genitalia formation and secondary sexual characteristics.