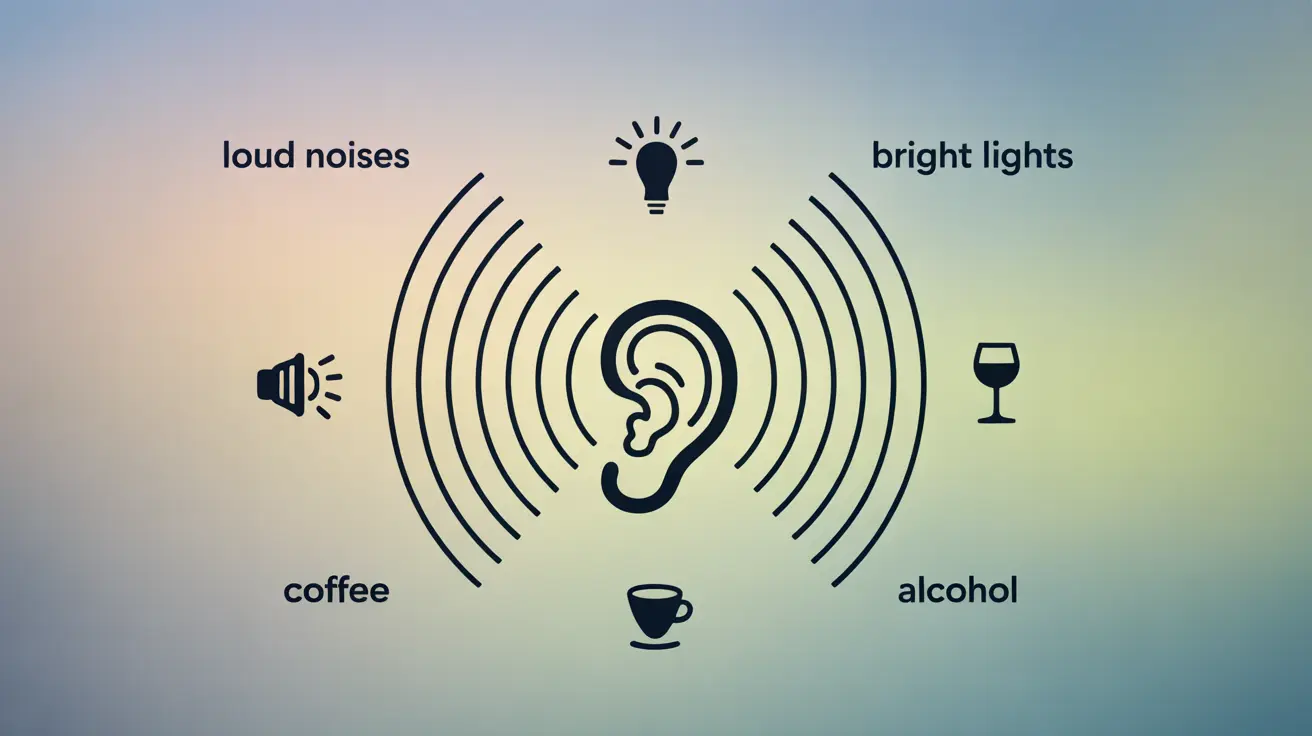
Living with tinnitus can be challenging, and many people find that certain factors can intensify their symptoms. Understanding what makes tinnitus worse is crucial for managing this persistent condition effectively and maintaining a better quality of life.
Whether you experience ringing, buzzing, or other phantom sounds in your ears, identifying and avoiding specific triggers can help reduce the impact of tinnitus on your daily activities. Let's explore the various factors that can aggravate tinnitus symptoms and discuss practical management strategies.
Common Environmental Triggers
Several environmental factors can significantly impact tinnitus severity:
- Loud noise exposure
- Sudden temperature changes
- High-altitude environments
- Bright or flickering lights
- Electromagnetic fields from electronic devices
Being aware of these environmental triggers allows you to take preventive measures and better control your symptoms. Using ear protection in noisy environments and maintaining a consistent ambient temperature can help minimize tinnitus flare-ups.
Lifestyle and Dietary Factors
Consuming Habits
What you consume can have a significant impact on tinnitus intensity:
- Caffeine and alcohol
- High-sodium foods
- Artificial sweeteners
- Processed foods
- Nicotine products
Monitoring your diet and keeping a symptom diary can help identify specific dietary triggers that affect your tinnitus.
Physical and Mental Health
Your overall health status can influence tinnitus severity:
- High blood pressure
- Poor sleep habits
- Stress and anxiety
- Physical exhaustion
- Neck and jaw tension
Medical Considerations
Medications
Certain medications may worsen tinnitus symptoms:
- Aspirin and NSAIDs
- Some antibiotics
- Certain antidepressants
- Diuretics
- Some cancer medications
Always consult with your healthcare provider before making any changes to your medication regimen, even if you suspect it's affecting your tinnitus.
Physical Conditions
Various health conditions can exacerbate tinnitus:
- Ear infections
- Earwax buildup
- Cardiovascular problems
- Temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disorders
- Head or neck injuries
Managing Tinnitus Effectively
Taking proactive steps to manage your tinnitus can help reduce its impact:
- Use sound therapy or white noise
- Practice stress reduction techniques
- Maintain good sleep hygiene
- Stay physically active
- Consider cognitive behavioral therapy
Frequently Asked Questions
What everyday things can make tinnitus worse or more noticeable?
Common daily factors that can intensify tinnitus include exposure to loud noises, stress, lack of sleep, caffeine consumption, and certain medications. Environmental factors like bright lights and sudden temperature changes can also affect symptoms.
Are there certain foods, drinks, or medications that can worsen tinnitus symptoms?
Yes, caffeine, alcohol, high-sodium foods, and artificial sweeteners can aggravate tinnitus. Some medications, including aspirin, certain antibiotics, and antidepressants, may also worsen symptoms. Always discuss medication concerns with your healthcare provider.
How does stress or lack of sleep affect tinnitus, and what can I do to manage it?
Both stress and poor sleep can significantly intensify tinnitus symptoms. Managing these factors through relaxation techniques, maintaining a regular sleep schedule, and practicing good sleep hygiene can help reduce tinnitus severity.
Can cleaning my ears or removing earwax help reduce the ringing in my ears?
While excessive earwax can worsen tinnitus, you should avoid cleaning your ears at home with cotton swabs or other objects. Instead, have a healthcare professional safely remove earwax buildup if necessary.
When should I see a doctor about my tinnitus symptoms?
Seek medical attention if your tinnitus is sudden, severe, or accompanied by hearing loss, dizziness, or pain. Also consult a doctor if tinnitus significantly affects your daily life or causes emotional distress.
Remember that while tinnitus can be challenging to manage, understanding your triggers and working with healthcare professionals can help you develop effective coping strategies for better symptom control.