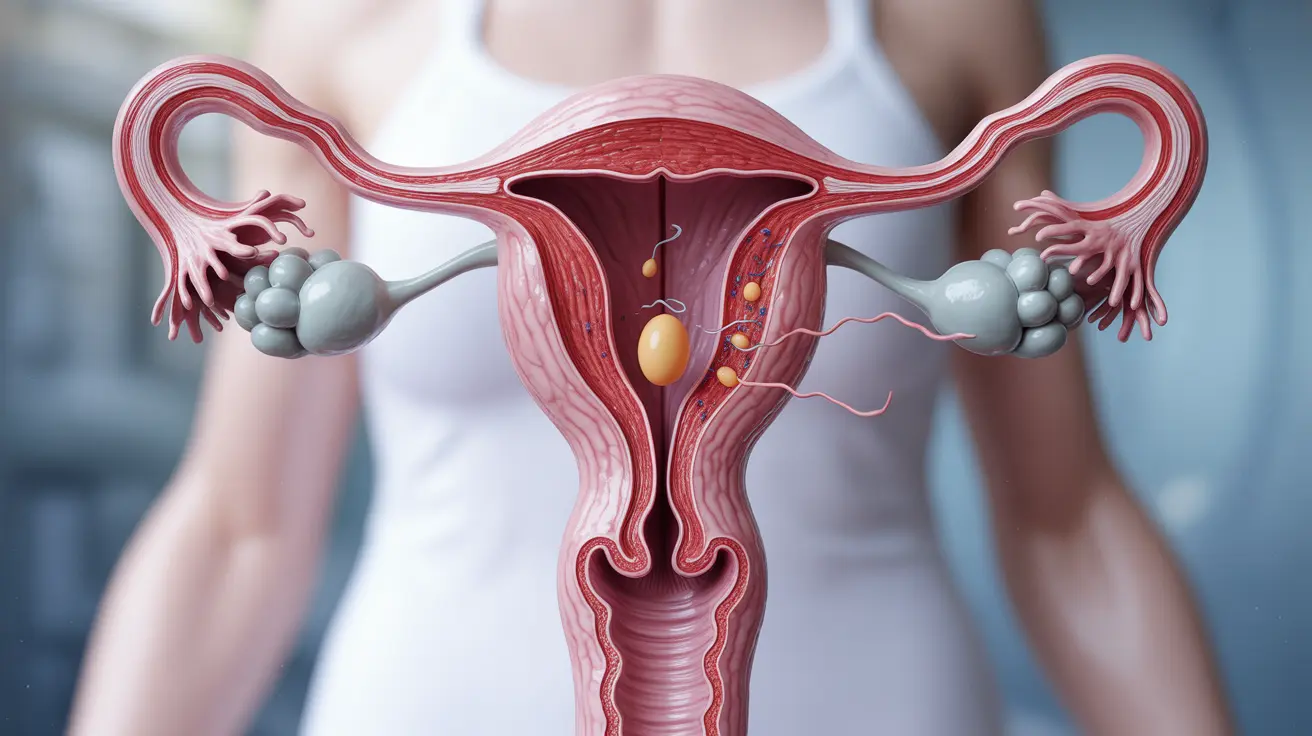
Fertilization is a crucial biological process that marks the beginning of pregnancy. Understanding where and how fertilization occurs can help individuals better comprehend reproductive health and fertility. This article explores the specific location of fertilization in the female reproductive system and the fascinating journey that follows.
The Primary Site of Fertilization
Fertilization typically occurs in the fallopian tubes, specifically in the ampulla region. These trumpet-shaped tubes extend from the ovaries to the uterus and provide the optimal environment for sperm to meet and fertilize an egg. The fallopian tubes' unique structure and conditions make them the perfect location for this vital process.
The Anatomy of Fertilization
The fallopian tubes contain specialized cells that create an environment conducive to fertilization. These cells produce nutrients and secretions that support both the egg and sperm cells. The tube's inner lining features tiny hair-like projections called cilia, which help move the egg and eventual fertilized embryo toward the uterus.
The Journey to Fertilization
After ovulation, the egg is released from the ovary and swept into the nearby fallopian tube. Meanwhile, sperm must travel through the cervix and uterus to reach the fallopian tube. Only the strongest and healthiest sperm complete this journey, which can take anywhere from 30 minutes to several hours.
The Critical Timeline
The window for successful fertilization is relatively brief. Once released, an egg remains viable for approximately 12-24 hours. Sperm can survive in the female reproductive tract for up to five days under optimal conditions, though their fertility peaks within the first 48-72 hours after ejaculation.
From Fertilization to Implantation
After fertilization occurs, the newly formed zygote begins a remarkable journey. As it travels down the fallopian tube toward the uterus, it undergoes several cell divisions, developing into a multi-celled structure called a blastocyst. This journey typically takes about 5-7 days, during which the uterine lining prepares for potential implantation.
When Natural Fertilization Isn't Possible
Sometimes, natural fertilization in the fallopian tubes may not be possible due to various medical conditions. In such cases, assisted reproductive technologies like in vitro fertilization (IVF) can help achieve pregnancy by bypassing the fallopian tubes entirely.
Frequently Asked Questions
Where in the female reproductive system does fertilization usually occur?
Fertilization typically occurs in the fallopian tubes, specifically in the ampulla section, which is the widest part of the tube located near the ovary.How does the fertilized egg travel from the fallopian tube to the uterus?
The fertilized egg moves through the fallopian tube aided by the tube's muscular contractions and the sweeping motion of tiny hair-like structures called cilia. This journey typically takes 5-7 days.What happens if the fallopian tubes are blocked or damaged—can fertilization still happen naturally?
Natural fertilization cannot occur with blocked or damaged fallopian tubes since sperm cannot reach the egg. In these cases, IVF may be necessary to achieve pregnancy.How long after ovulation is the egg viable for fertilization in the fallopian tube?
An egg remains viable for fertilization for approximately 12-24 hours after ovulation. This creates a relatively short window for successful fertilization to occur.What is the difference between fertilization in natural conception and in vitro fertilization (IVF)?
In natural conception, fertilization occurs in the fallopian tube, while IVF involves fertilizing the egg with sperm in a laboratory setting before transferring the resulting embryo directly into the uterus.