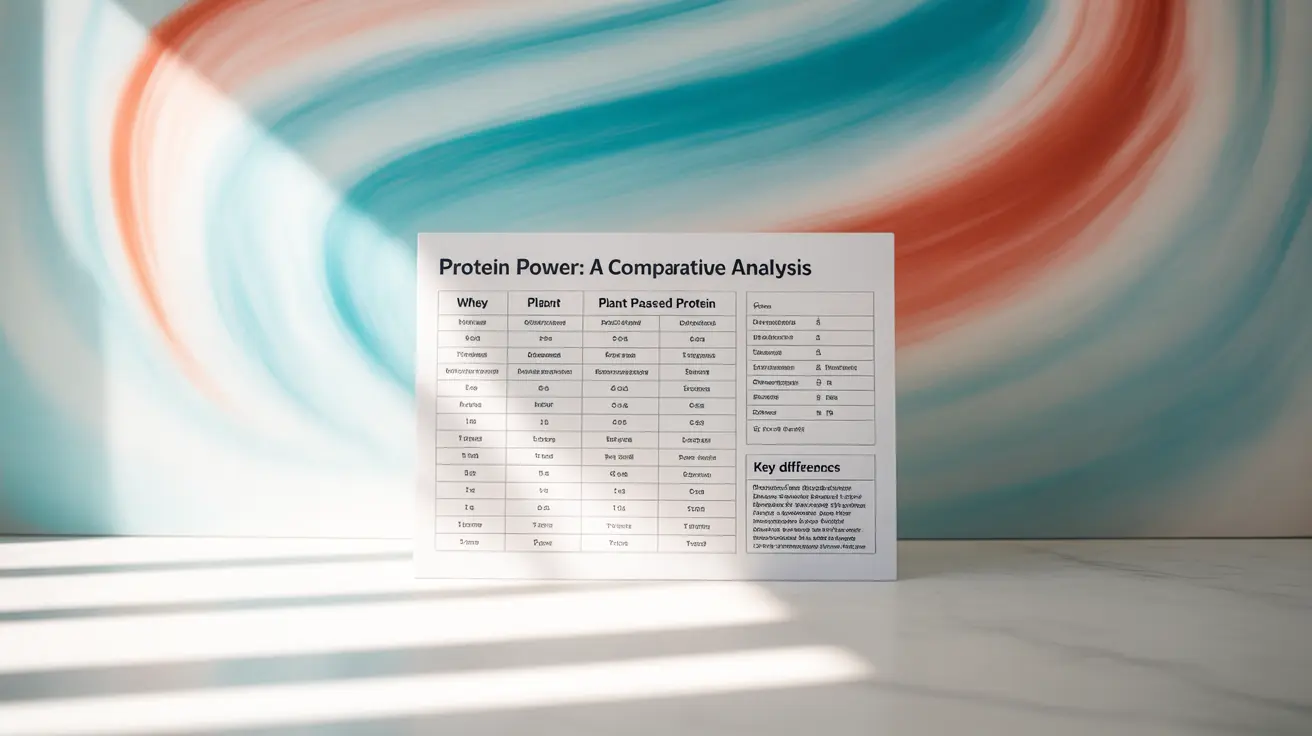
Choosing between whey and plant protein can significantly impact your fitness goals, health needs, and environmental footprint. As protein supplementation becomes increasingly popular, understanding the key differences between these two protein sources is essential for making an informed decision about which one best suits your needs.
This comprehensive guide explores the fundamental differences between whey and plant protein, examining their effectiveness, digestibility, and environmental impact to help you make the best choice for your lifestyle and goals.
Nutritional Composition and Amino Acid Profiles
Whey protein is derived from milk and contains all nine essential amino acids in optimal ratios, making it a complete protein source. It's particularly rich in leucine, an amino acid crucial for muscle protein synthesis.
Plant proteins, which can come from sources like pea, rice, hemp, or soy, may have varying amino acid profiles. While some plant proteins like soy are complete proteins, others may need to be combined to achieve a full amino acid spectrum. Modern plant protein blends often address this by combining multiple sources to create a complete amino acid profile.
Muscle Building and Recovery Potential
Both whey and plant proteins can effectively support muscle growth and recovery, though they may work through slightly different mechanisms. Whey protein is rapidly absorbed and has a high leucine content, making it particularly effective for immediate post-workout recovery.
Plant proteins, while generally absorbed more slowly, can be equally effective for muscle building when consumed in appropriate amounts. Recent studies have shown that plant protein blends, when properly formulated, can match whey protein's muscle-building capabilities.
Digestibility and Allergen Considerations
Whey protein's high digestibility makes it an excellent choice for many athletes. However, it may not be suitable for those with dairy allergies or lactose intolerance, even in isolate form.
Plant proteins are generally more easily tolerated by those with dairy sensitivities and may cause less digestive discomfort. However, some individuals might be sensitive to specific plant protein sources, such as soy or wheat-based proteins.
Taste, Texture, and Mixability
Whey protein is known for its smooth texture and pleasant taste, especially in vanilla and chocolate flavors. It typically blends well with liquids and can create a creamy consistency in shakes.
Plant proteins have made significant advances in taste and texture, though they may have a slightly grainier texture compared to whey. Modern formulations often include natural flavoring and texturing agents to improve the overall experience.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Plant proteins generally have a lower environmental impact, requiring fewer resources and producing fewer greenhouse gas emissions during production. They often need less water and land use compared to dairy-based proteins.
Whey protein, being a dairy product, has a larger environmental footprint. However, as it's a by-product of cheese production, it can be argued that it helps reduce dairy industry waste.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main differences between whey protein and plant protein in terms of muscle building and amino acid content? Whey protein contains all essential amino acids and is particularly rich in leucine, while plant proteins may vary in their amino acid profiles. Both can support muscle building, but whey is typically faster-absorbing and has a more complete amino acid profile naturally.
Is plant protein as effective as whey protein for weight loss and muscle recovery? Yes, plant protein can be equally effective for weight loss and muscle recovery when consumed in appropriate amounts. While whey may have faster absorption rates, plant proteins can provide similar benefits, especially when using protein blends designed to provide complete amino acid profiles.
Can people with lactose intolerance or dairy allergies safely use plant-based protein powders instead of whey? Yes, plant-based protein powders are generally safe alternatives for those with lactose intolerance or dairy allergies. They're naturally dairy-free and typically cause fewer allergic reactions, though individuals should still check for other potential allergens in the specific product they choose.
How do the taste and texture of whey protein compare to those of plant-based protein powders? Whey protein typically has a smoother texture and mixes more easily with liquids. Plant proteins may have a slightly grainier texture and earthier taste, though modern formulations have significantly improved in both aspects through advanced processing and natural flavoring.
Which protein powder is more environmentally sustainable: whey or plant-based protein? Plant-based protein powders are generally more environmentally sustainable, requiring less water, land, and energy to produce while generating fewer greenhouse gas emissions compared to whey protein, which is derived from dairy production.