If you've ever eaten asparagus and noticed a distinct odor in your urine afterward, you're not alone. This peculiar phenomenon, often called the "asparagus effect," is a well-documented biological reaction that occurs when our bodies process this nutritious vegetable. Understanding why this happens can help demystify this common experience and reassure those who may be concerned about this natural occurrence.
The science behind asparagus-induced urine odor involves specific chemical compounds and how our bodies metabolize them. Let's explore the fascinating biological process behind this unique reaction and address common concerns about this harmless but notable effect.
The Science Behind Asparagus and Urine Odor
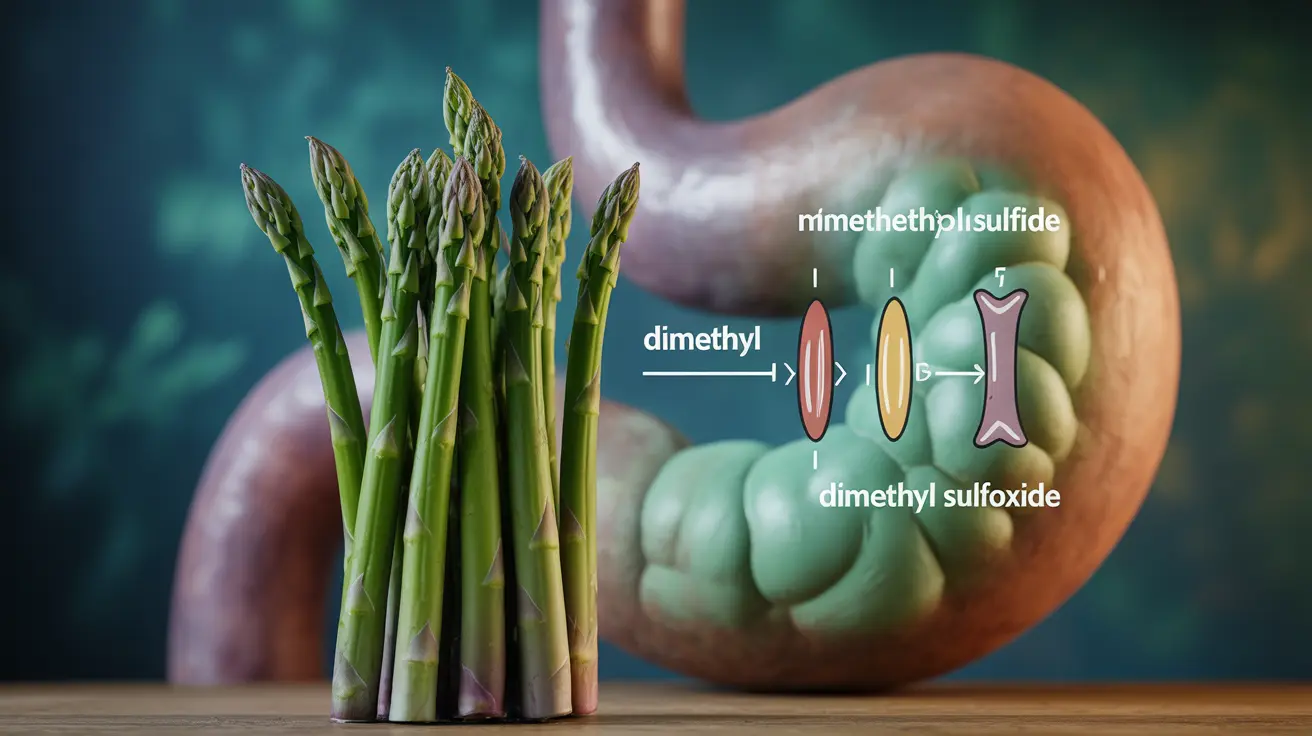
When we consume asparagus, our bodies break down specific sulfur-containing compounds, particularly asparagusic acid, which is unique to asparagus. During digestion, this compound is converted into various sulfur-containing metabolites, including methanethiol, dimethyl sulfide, and dimethyl sulfoxide. These volatile organic compounds are responsible for the characteristic smell in urine after eating asparagus.
The Chemical Process
The breakdown process begins almost immediately after consumption. Our digestive system metabolizes these compounds efficiently, which is why the distinctive odor can appear in urine as quickly as 15-30 minutes after eating asparagus. The speed of this process demonstrates how quickly our bodies process and eliminate these specific compounds.
Genetic Variations in Smell Perception
Interestingly, not everyone can detect the distinct odor in urine after eating asparagus. This variation is due to a genetic difference known as "specific anosmia." Some individuals lack the genetic ability to smell these particular sulfur compounds, even though their bodies are still producing them after consuming asparagus.
The Role of Genetics
Research suggests that approximately 40-50% of people cannot smell the distinctive odor in urine after eating asparagus. This genetic variation is similar to other inherited traits and doesn't indicate any health issues or concerns. It's simply a natural variation in human genetic makeup.
Health and Safety Considerations
The production of these sulfur compounds after eating asparagus is completely normal and harmless. In fact, asparagus itself is highly nutritious, containing essential vitamins, minerals, and fiber. The odor-producing reaction is simply a side effect of your body efficiently processing these beneficial nutrients.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why does eating asparagus make my urine smell like sulfur?
Your urine smells different after eating asparagus because your body breaks down asparagusic acid into sulfur-containing compounds. These volatile organic compounds create the distinctive odor when released in urine.
How soon after eating asparagus does the urine odor appear and how long does it last?
The odor typically appears within 15-30 minutes after eating asparagus and can last for several hours, depending on your individual metabolism and hydration levels.
Why can some people not smell the asparagus odor in their urine?
This is due to a genetic variation called specific anosmia. About 40-50% of people lack the genes necessary to detect these particular sulfur compounds, though their bodies still produce them.
Is the smelly urine caused by asparagus harmful to my health?
No, the odor is completely harmless and simply indicates that your body is properly metabolizing the natural compounds found in asparagus.
How much asparagus do I need to eat to cause the distinctive urine smell?
Even a small amount of asparagus, as little as a few spears, can produce the distinctive odor in urine. The intensity may vary based on the amount consumed and individual metabolism.