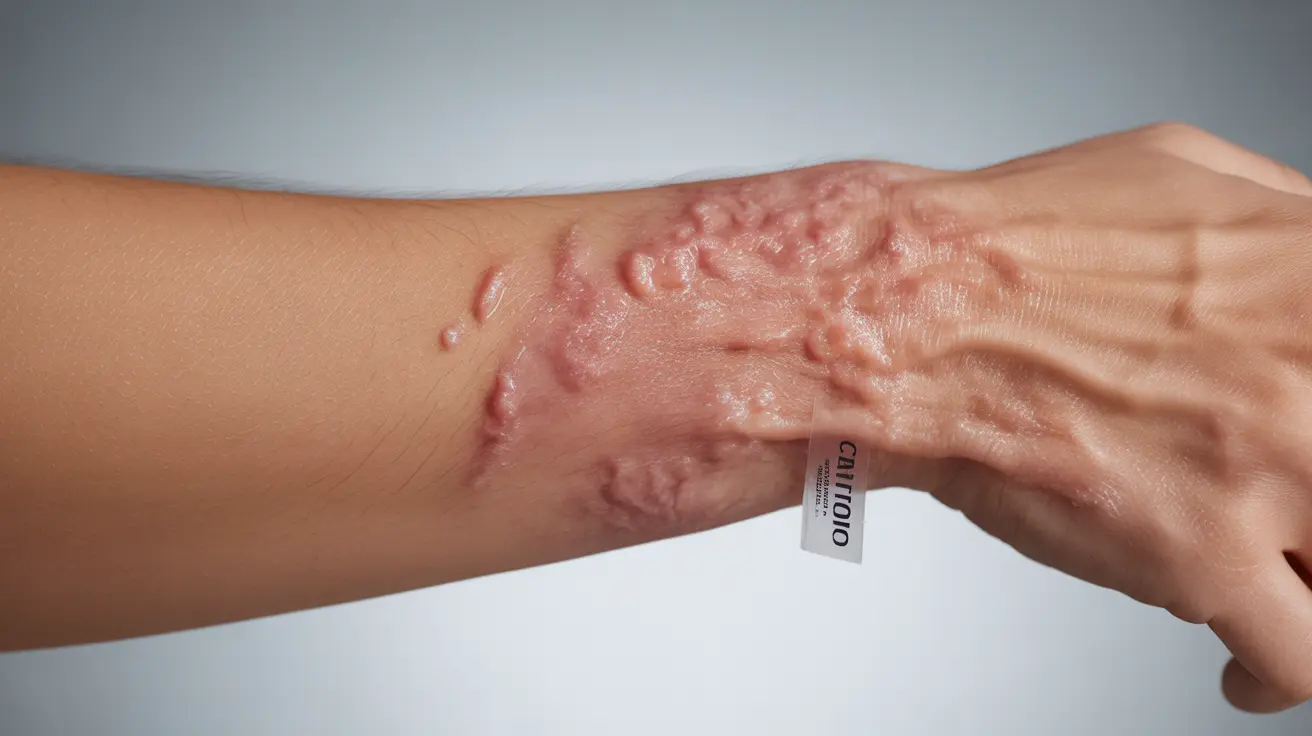
Living with severe eczema can be challenging, especially when conventional treatments like moisturizers and basic creams no longer provide adequate relief. Understanding the full spectrum of available treatments is crucial for effectively managing this chronic skin condition and improving quality of life.
This comprehensive guide explores advanced treatment options for severe eczema, from powerful medications to innovative therapies, helping you make informed decisions about your care in partnership with healthcare providers.
Understanding Advanced Medication Options
Biologic Treatments
Biologic medications represent a breakthrough in severe eczema treatment. These targeted therapies work by modulating specific parts of the immune system that contribute to eczema symptoms. Dupilumab, the first FDA-approved biologic for moderate to severe eczema, has shown remarkable success in reducing inflammation and itching while improving sleep quality.
Systemic Medications
When topical treatments prove insufficient, oral or injectable medications may be prescribed. These include:
- Oral corticosteroids (short-term use only)
- Immunosuppressants like cyclosporine
- JAK inhibitors
- Oral antihistamines for itch relief
Optimizing Topical Treatments
Prescription-Strength Solutions
Topical treatments remain a cornerstone of eczema management. Advanced options include:
- High-potency topical corticosteroids for acute flares
- Topical calcineurin inhibitors (TCIs) for sensitive areas
- PDE4 inhibitors
- Barrier repair medications
Safe Application Techniques
Proper application of topical medications is crucial for effectiveness and safety. Using the fingertip unit method helps ensure appropriate dosing, while following prescribed treatment durations helps minimize potential side effects.
Advanced Therapeutic Approaches
Phototherapy Treatment
Controlled exposure to specific wavelengths of UV light can effectively reduce inflammation and itching. Different types of phototherapy may be recommended:
- Narrowband UVB
- PUVA (Psoralen plus UVA)
- Targeted phototherapy for specific areas
Wet Wrap Therapy
This intensive treatment involves applying medications and moisturizers under damp bandages or clothing. It's particularly effective for severe flares and can provide significant relief when done correctly.
Prevention and Maintenance Strategies
Trigger Management
Identifying and avoiding personal triggers is essential for long-term control. Common triggers include:
- Specific fabrics and materials
- Environmental allergens
- Stress
- Temperature changes
- Certain soaps and detergents
Skin Barrier Protection
Maintaining skin barrier function is crucial for preventing flares. This includes:
- Regular use of appropriate moisturizers
- Gentle cleansing practices
- Proper humidity control
- Protective clothing choices
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the most effective treatments for severe eczema when moisturizers and topical creams don't work? Biologic medications like dupilumab, systemic immunosuppressants, and phototherapy are often most effective for severe cases that don't respond to basic treatments. These options should be discussed with a healthcare provider to determine the best approach.
How do biologic drugs like dupilumab help treat moderate to severe eczema, and what are their side effects? Biologics target specific proteins in the immune system that cause inflammation. Dupilumab blocks interleukin proteins, reducing eczema symptoms. Common side effects may include injection site reactions, eye problems, and cold sores.
What role do topical corticosteroids and calcineurin inhibitors play in managing eczema symptoms safely? These medications reduce inflammation and itching when used as directed. Corticosteroids provide quick relief but require careful monitoring, while calcineurin inhibitors are safer for long-term use, especially on sensitive areas.
Can phototherapy or wet wrap therapy improve severe eczema flare-ups, and how are they used? Yes, both treatments can be effective. Phototherapy involves controlled UV light exposure in a medical setting, while wet wrap therapy uses damp bandages over medications to enhance absorption and provide relief.
How important is avoiding triggers and maintaining skin hydration in preventing eczema flare-ups? Trigger avoidance and proper skin hydration are fundamental to preventing flares. Consistent moisturizing, trigger identification, and lifestyle modifications can significantly reduce the frequency and severity of episodes.