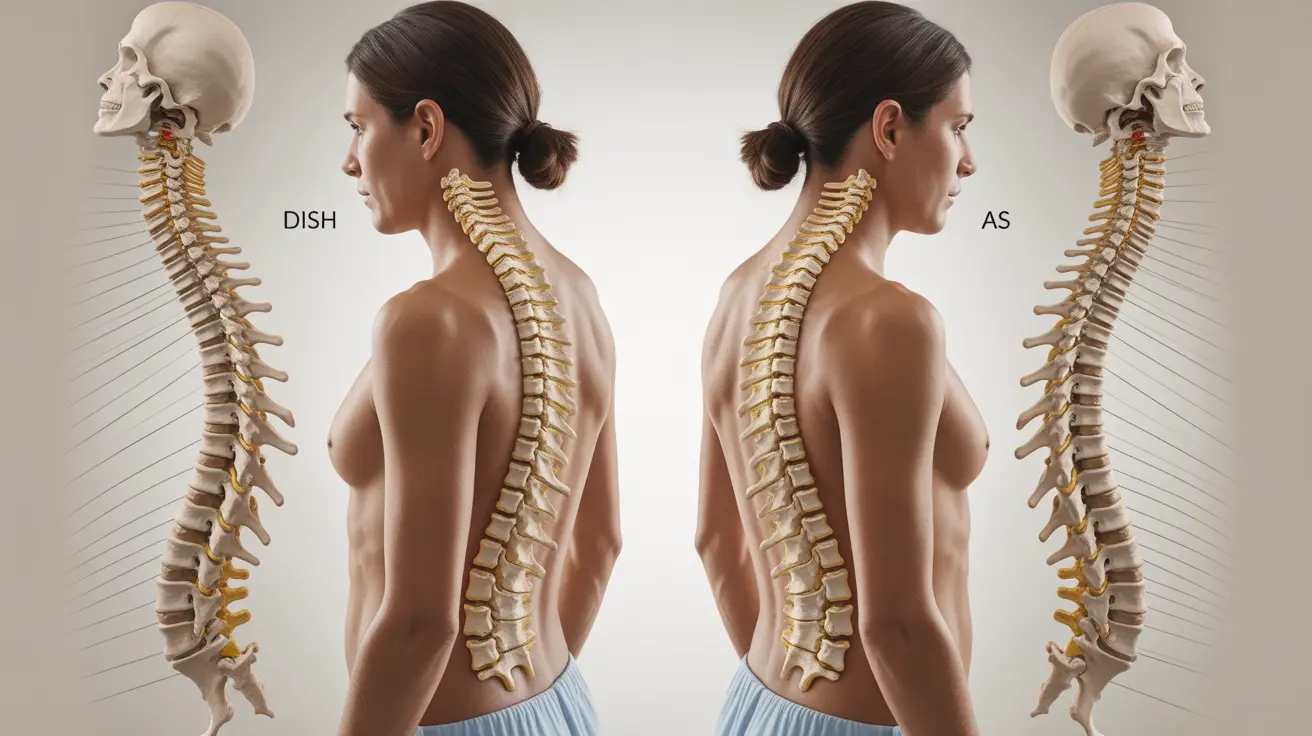
Living with back pain and stiffness can be challenging, especially when trying to determine the underlying cause. Two conditions that often cause similar symptoms are diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis (DISH) and ankylosing spondylitis (AS). While these conditions may share some characteristics, understanding their distinct features is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment.
In this comprehensive guide, we'll explore the key differences between DISH and ankylosing spondylitis, including their symptoms, diagnostic approaches, and treatment options. This information will help you better understand these conditions and work more effectively with your healthcare provider.
Understanding DISH and Ankylosing Spondylitis
DISH is a condition characterized by the hardening of ligaments and tendons, particularly along the spine. It typically affects older adults and is more common in men. In contrast, ankylosing spondylitis is an inflammatory arthritis that primarily affects the spine and typically begins in early adulthood.
Key Differences in Symptoms
While both conditions affect the spine, their symptom patterns differ significantly:
DISH Symptoms
- Stiffness and pain, particularly in the upper back
- Morning stiffness that improves with movement
- Difficulty swallowing (in some cases)
- Limited range of motion in the spine
- Pain at points where tendons and ligaments attach to bones
Ankylosing Spondylitis Symptoms
- Chronic lower back and hip pain
- Morning stiffness that improves with exercise
- Fatigue and low-grade fever
- Eye inflammation (uveitis)
- Pain that improves with activity and worsens with rest
Diagnostic Approaches
Healthcare providers use different methods to diagnose these conditions:
DISH Diagnosis
- X-rays showing distinctive bone growths
- Evaluation of symptoms and medical history
- Physical examination
- No specific blood tests required
AS Diagnosis
- MRI and X-ray imaging
- Blood tests for HLA-B27 genetic marker
- Assessment of inflammatory markers
- Comprehensive physical examination
Treatment Strategies and Management
Both conditions require different approaches to treatment:
Managing DISH
- Pain management medications
- Physical therapy exercises
- Weight management
- Proper posture techniques
- Heat or cold therapy
Managing Ankylosing Spondylitis
- NSAIDs for inflammation
- Biological medications
- Regular exercise programs
- Physical therapy
- Posture correction
Living with These Conditions
While both conditions are chronic, they can be managed effectively with proper care and lifestyle modifications. Regular exercise, maintaining a healthy weight, and working closely with healthcare providers are essential for both conditions.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What are the main differences in symptoms between diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis (DISH) and ankylosing spondylitis (AS)?
DISH typically affects older adults and causes upper back stiffness and pain, while AS usually begins in early adulthood and primarily affects the lower back and hips. AS is inflammatory in nature, while DISH involves the hardening of ligaments and tendons.
- How do doctors diagnose DISH compared to ankylosing spondylitis?
DISH is primarily diagnosed through X-rays showing characteristic bone growths, while AS diagnosis involves multiple tools including MRI, blood tests for the HLA-B27 genetic marker, and inflammatory marker testing.
- What treatment options are available for managing pain and stiffness in DISH versus ankylosing spondylitis?
DISH treatment focuses on pain management and physical therapy, while AS treatment includes anti-inflammatory medications, biological drugs, and specific exercise programs designed to maintain spinal flexibility.
- Can lifestyle changes like weight loss and exercise help with DISH and ankylosing spondylitis?
Yes, lifestyle changes are beneficial for both conditions. Weight management and appropriate exercise can help reduce symptoms in DISH, while regular exercise is crucial for maintaining flexibility and managing pain in AS.
- What complications are common with DISH and ankylosing spondylitis, and how do they differ?
DISH complications often include difficulty swallowing and limited spinal mobility, while AS can lead to spinal fusion, reduced chest expansion, and eye inflammation. AS may also increase the risk of cardiovascular issues.