Glucagon injection is a critical emergency medication used to treat severe hypoglycemia (dangerously low blood sugar) in people with diabetes. Understanding how to properly use and administer this life-saving treatment is essential for caregivers, family members, and healthcare providers who support individuals with diabetes.
This comprehensive guide will walk you through everything you need to know about glucagon injections, from proper administration techniques to storage requirements, ensuring you're prepared for emergency situations.
Understanding Glucagon and Its Purpose
Glucagon is a hormone that works opposite to insulin, raising blood sugar levels by triggering the liver to release stored glucose. When someone with diabetes experiences severe hypoglycemia and cannot consume sugar orally, a glucagon injection can be life-saving.
The medication is particularly crucial when a person is unconscious, experiencing seizures, or unable to safely swallow due to severe low blood sugar.
Types of Glucagon Products Available
Modern glucagon emergency kits come in several forms:
- Pre-mixed auto-injectors (like GlucaGen® HypoKit)
- Nasal spray formulations (Baqsimi®)
- Traditional mix-and-inject kits
Each type has specific advantages, with newer formulations designed for easier use during stressful emergency situations.
Proper Administration Technique
Before Administration
First, check for:
- Signs of severe hypoglycemia
- The glucagon kit's expiration date
- Kit integrity and proper storage conditions
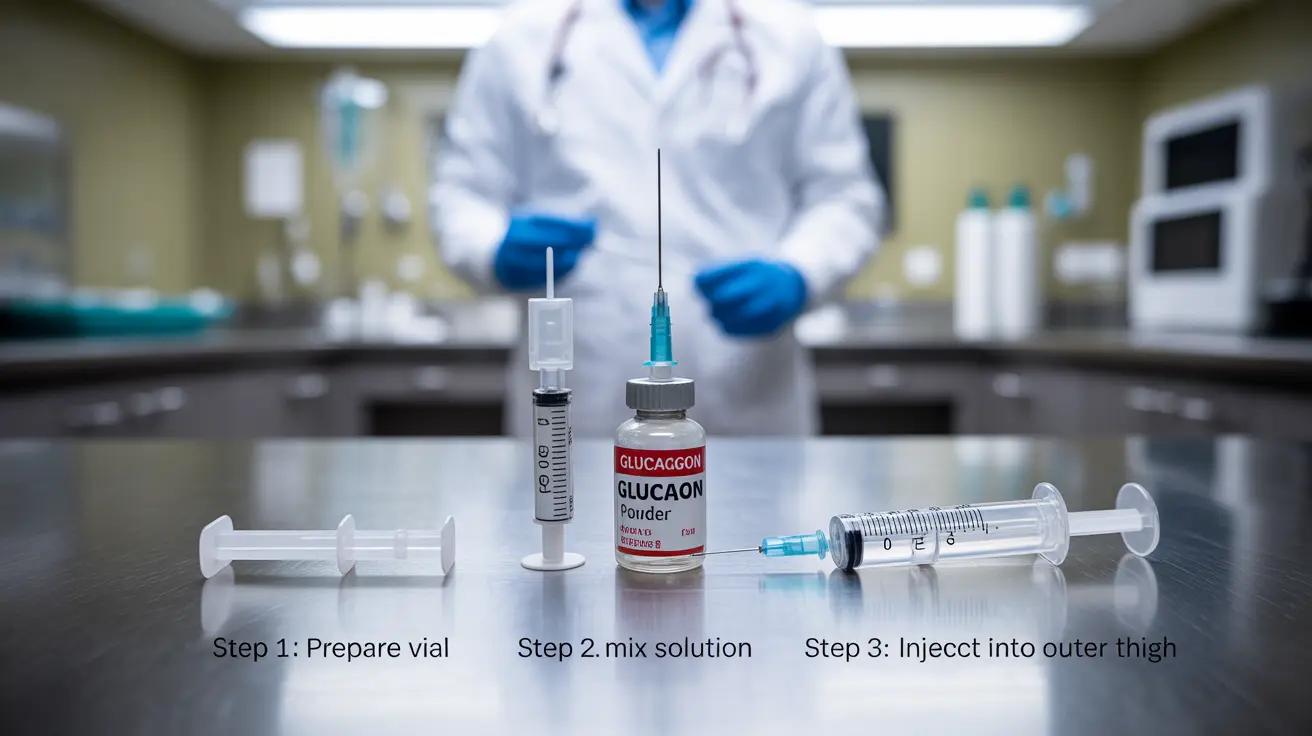
Steps for Injection
For traditional kits:
- Remove flip-off seal from the vial
- Inject the diluent into the powder vial
- Gently mix until the solution is clear
- Draw the proper dose into the syringe
- Inject into the outer thigh, upper arm, or buttocks
For auto-injectors, follow the device-specific instructions, which typically involve fewer steps and are designed for quick administration.
Post-Injection Care
After administering glucagon:
- Turn the person on their side
- Call emergency services
- Monitor for consciousness
- Be prepared to give glucose once the person is alert
- Document the incident for medical records
Storage and Maintenance
Proper storage is crucial for maintaining glucagon's effectiveness:
- Store at room temperature (68-77°F/20-25°C)
- Keep away from direct light
- Check expiration dates monthly
- Replace kits before they expire
- Keep in an easily accessible location
Frequently Asked Questions
What is glucagon injection used for and when should it be administered?
Glucagon injection is used to treat severe hypoglycemia in people with diabetes when they cannot take sugar by mouth. It should be administered when someone is unconscious, having seizures, or unable to safely swallow due to low blood sugar.
How do I properly prepare and give a glucagon injection in an emergency?
For traditional kits, reconstitute the powder with the provided diluent, ensure complete mixing, and inject into the outer thigh, upper arm, or buttocks. For auto-injectors, follow the device's specific instructions. Always call emergency services after administration.
What types of glucagon products are available and how do they differ?
Available products include traditional mix-and-inject kits, pre-mixed auto-injectors, and nasal spray formulations. Auto-injectors and nasal sprays are designed for easier use, while traditional kits require mixing before use but may be more cost-effective.
What should I do after giving a glucagon injection to someone with severe low blood sugar?
Place the person in the recovery position, call emergency services, monitor their consciousness, and prepare to give oral glucose once they're alert and able to swallow safely. Document the incident for medical records.
How should glucagon injection kits be stored and when should they be replaced?
Store kits at room temperature away from direct light. Check expiration dates monthly and replace before expiration. Keep in an easily accessible location known to family members and caregivers. Replace any kits that show signs of damage or discoloration.