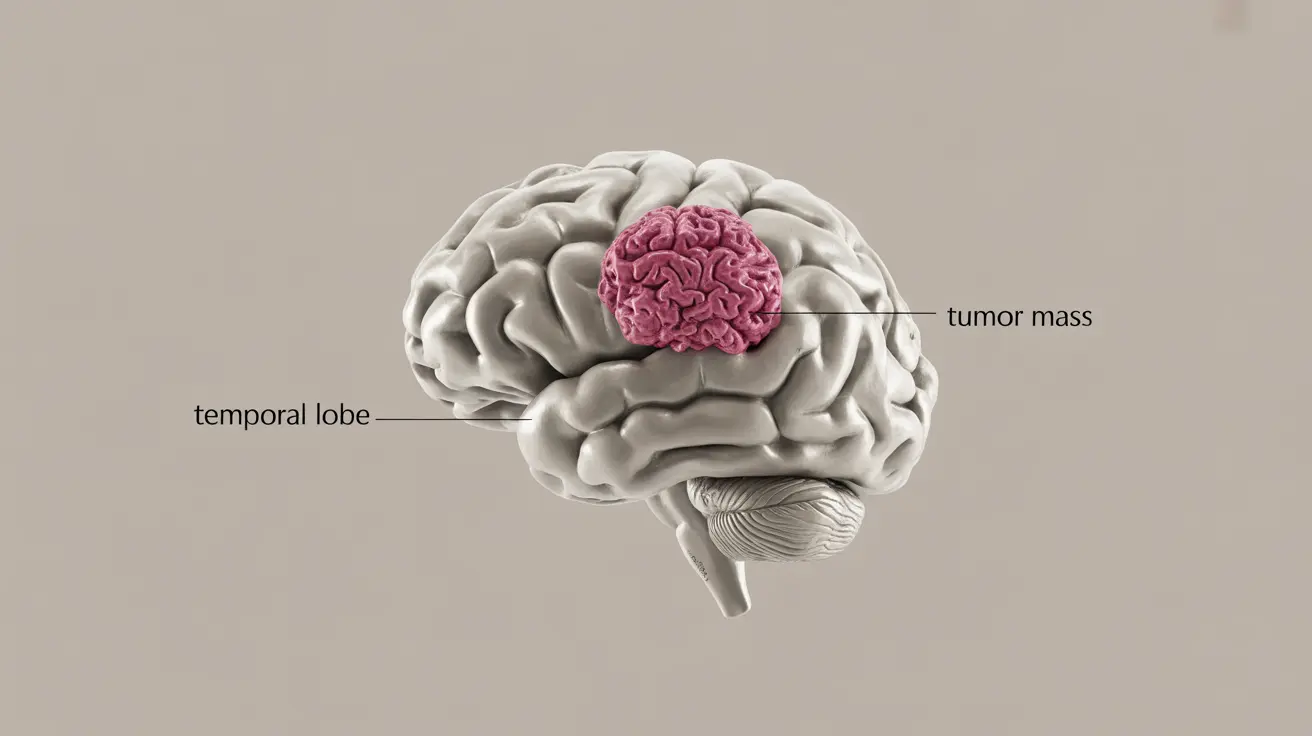
A mass on the brain, also known as a brain lesion or tumor, is an abnormal growth of tissue that can develop within the brain or surrounding areas. These masses can vary significantly in size, location, and whether they're benign (non-cancerous) or malignant (cancerous). Understanding the signs, diagnosis process, and available treatments is crucial for anyone concerned about this condition.
Early detection and proper medical intervention are key factors in managing brain masses effectively. This comprehensive guide will explore the essential aspects of brain masses, from initial symptoms to treatment options and recovery expectations.
Common Signs and Symptoms of Brain Masses
Brain masses can produce various symptoms depending on their size, location, and growth rate. Early recognition of these warning signs is crucial for timely medical intervention:
- Persistent headaches that worsen over time
- Changes in vision or hearing
- Unexplained nausea and vomiting
- Balance and coordination problems
- Seizures or convulsions
- Memory issues or confusion
- Changes in personality or behavior
- Difficulty speaking or finding words
Diagnostic Process and Medical Tests
When a brain mass is suspected, healthcare providers typically follow a comprehensive diagnostic approach:
Initial Assessment
The process usually begins with a detailed medical history and neurological examination. Doctors will evaluate cognitive function, balance, coordination, and reflexes.
Imaging Studies
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging)
- CT (Computed Tomography) scan
- PET (Positron Emission Tomography) scan
- Specialized brain scans with contrast
Additional Tests
Depending on initial findings, doctors may recommend:
- Biopsy procedures
- Blood tests
- Cerebrospinal fluid analysis
- Neurological function tests
Treatment Approaches
Treatment plans for brain masses are highly individualized and depend on several factors, including:
Surgical Options
Surgery is often the primary treatment approach when possible. Modern surgical techniques include:
- Traditional craniotomy
- Minimally invasive procedures
- Laser ablation
- Stereotactic radiosurgery
Non-Surgical Treatments
Additional treatment options may include:
- Radiation therapy
- Chemotherapy
- Targeted drug therapy
- Immunotherapy
Prevention and Risk Factors
While not all brain masses can be prevented, understanding risk factors is important:
- Family history of brain tumors
- Exposure to certain chemicals or radiation
- Age and gender considerations
- Previous cancer history
- Immune system conditions
Recovery and Rehabilitation
The recovery process varies significantly among patients and depends on factors such as:
- Type and location of the mass
- Treatment method used
- Overall health status
- Support system and rehabilitation resources
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the early warning signs and symptoms of a mass on the brain? Early warning signs include persistent headaches, vision changes, unexplained nausea, balance problems, seizures, and cognitive changes. Any combination of these symptoms warrants immediate medical attention.
How is a brain mass diagnosed and what tests will my doctor recommend? Diagnosis typically involves neurological examination, advanced imaging (MRI, CT, PET scans), and possibly biopsy. Your doctor will choose specific tests based on your symptoms and initial findings.
What are the treatment options for a benign or malignant brain mass? Treatment options include surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, and targeted treatments. The specific approach depends on the mass type, location, size, and your overall health status.
Can a mass on the brain be prevented and are there any known causes or risk factors? While not all brain masses are preventable, risk factors include genetic predisposition, radiation exposure, and certain medical conditions. Maintaining overall health and avoiding known risk factors can help reduce risk.
How long does recovery take after treatment for a brain mass and what can I expect during the healing process? Recovery time varies significantly depending on the treatment type and extent of the procedure. Most patients require several weeks to months for initial recovery, followed by ongoing rehabilitation if needed. The process may include physical therapy, occupational therapy, and regular monitoring.