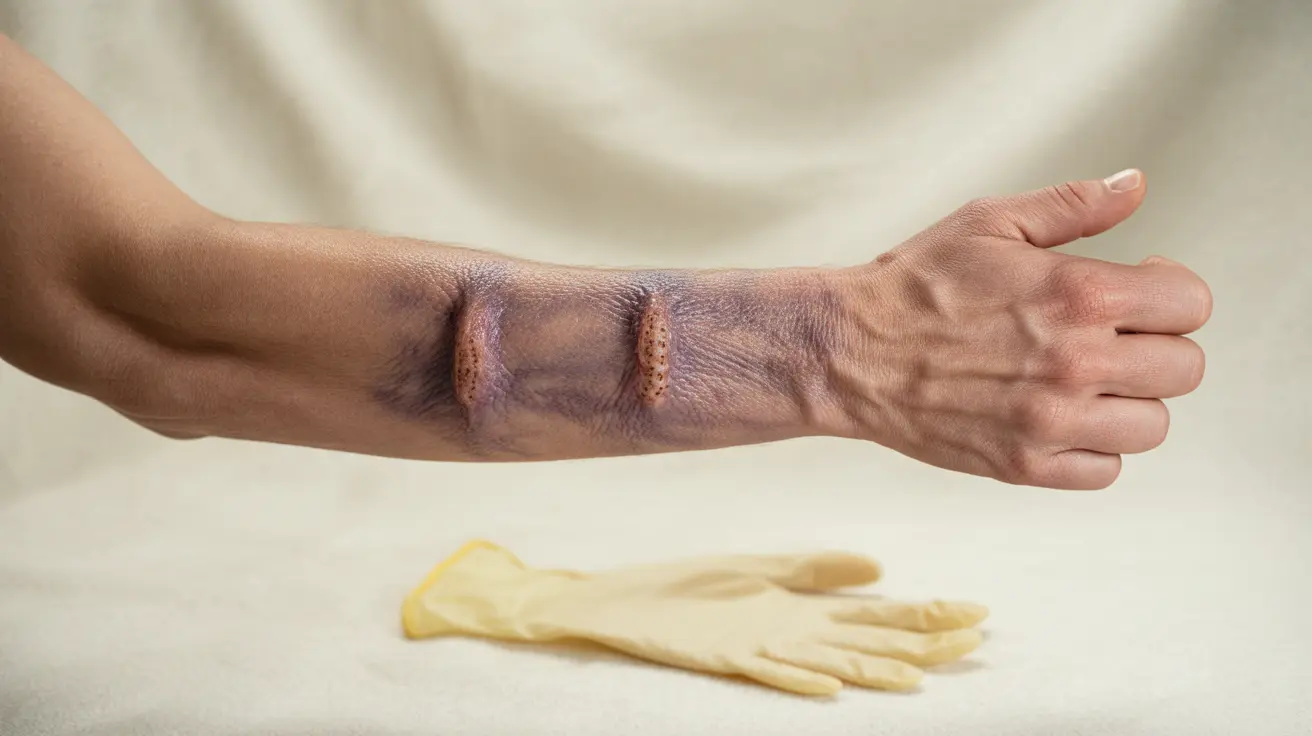
A rattlesnake bite is a serious medical emergency that requires immediate attention and professional care. Understanding the proper response to a rattlesnake bite can mean the difference between life and death. This comprehensive guide covers essential information about rattlesnake bite symptoms, treatment, and prevention strategies.
While rattlesnake bites are relatively rare, they account for the majority of snakebite-related deaths in North America. Quick recognition of symptoms and proper first aid are crucial for improving outcomes after a bite occurs.
Understanding Rattlesnake Bite Symptoms
The symptoms of a rattlesnake bite typically develop rapidly and can vary in severity. Immediate signs include:
- Intense pain and burning sensation at the bite site
- Two puncture marks from the fangs
- Immediate swelling and discoloration
- Numbness or tingling around the wound
As time progresses, additional symptoms may develop:
- Difficulty breathing
- Rapid heart rate
- Weakness or dizziness
- Nausea and vomiting
- Blurred vision
- Excessive sweating
Critical First Aid Steps
When someone experiences a rattlesnake bite, taking the right actions immediately is essential:
Do These Immediately
- Keep the affected area below heart level
- Remove any constricting items (jewelry, tight clothing)
- Stay as still as possible to slow venom spread
- Call 911 or get emergency medical transport
- Note the time of the bite for medical personnel
Important Safety Considerations
Proper first aid also involves avoiding certain dangerous practices that can worsen the situation:
- Don't apply a tourniquet
- Don't attempt to suck out the venom
- Don't apply ice to the bite area
- Don't try to capture the snake
- Don't take pain medications before reaching the hospital
The Role of Antivenom Treatment
Antivenom is the primary and most effective treatment for rattlesnake bites. This specialized medication works by neutralizing the snake's venom in the victim's body. The sooner antivenom is administered, the better the outcome typically is.
Medical professionals will determine the appropriate amount of antivenom based on several factors:
- Severity of symptoms
- Size of the snake
- Time elapsed since the bite
- Patient's overall health condition
Prevention Strategies
Taking proper precautions can significantly reduce your risk of rattlesnake encounters:
- Stay on marked trails while hiking
- Wear appropriate footwear (thick boots)
- Use a walking stick to probe areas ahead
- Avoid reaching into areas you can't see clearly
- Listen for warning rattles
- Keep your yard clear of debris and tall grass
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the immediate symptoms to watch for after a rattlesnake bite? Immediate symptoms include severe pain, swelling around the bite marks, discoloration of the skin, and possible difficulty breathing. You may also experience nausea, weakness, and tingling sensations around the bite area.
How should I provide first aid if someone is bitten by a rattlesnake? Keep the person calm and still, remove any constricting items near the bite area, keep the affected limb below heart level, and seek immediate emergency medical care. Don't attempt to suck out venom or apply tourniquets.
Why is antivenom treatment important after a rattlesnake bite? Antivenom is crucial because it's the only effective treatment that can neutralize rattlesnake venom in the body. Without antivenom, the venom can cause severe tissue damage, organ failure, and potentially death.
What should I avoid doing if I or someone else is bitten by a rattlesnake? Avoid applying tourniquets, ice, or electric shock. Don't try to suck out the venom or make incisions. Don't take aspirin or other pain medications, and don't attempt to catch the snake.
How can I prevent rattlesnake bites when hiking or spending time outdoors? Stay on designated trails, wear proper boots and long pants, use hiking poles, remain alert, and listen for warning rattles. Avoid reaching into brush or rock crevices where snakes might hide, and keep your distance if you encounter a snake.