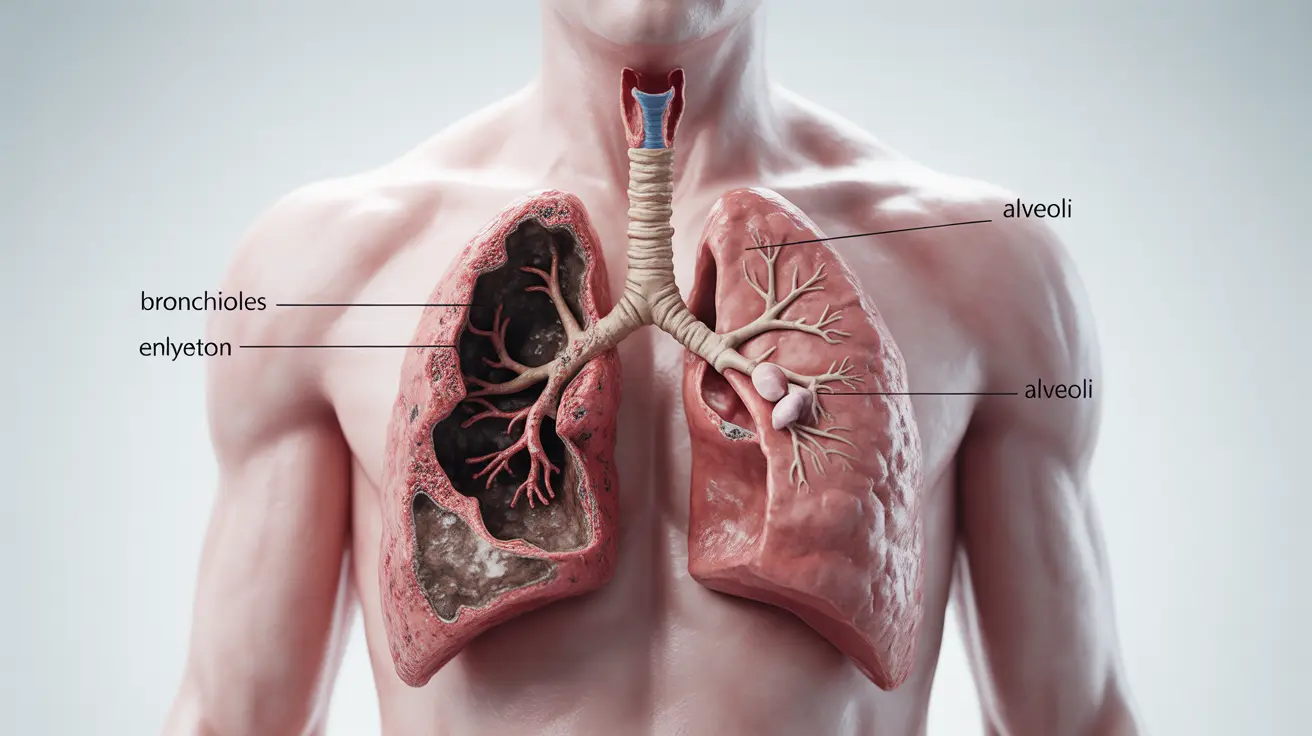
Severe emphysema is a serious progressive lung condition that significantly impacts breathing and quality of life. As part of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), severe emphysema occurs when the air sacs in the lungs become damaged, making it increasingly difficult to breathe and perform daily activities.
Understanding the complexities of severe emphysema, its symptoms, and available treatment options is crucial for patients and their caregivers. This comprehensive guide explores the key aspects of managing this challenging condition and improving quality of life.
Common Symptoms of Severe Emphysema
Severe emphysema presents with several distinctive symptoms that can significantly affect daily functioning:
- Severe shortness of breath, especially during physical activity
- Chronic cough with or without mucus
- Persistent wheezing
- Chest tightness and discomfort
- Frequent respiratory infections
- Unexplained weight loss
- Bluish tint to lips or fingernails (cyanosis)
As the condition progresses, these symptoms typically become more pronounced, making routine activities increasingly challenging.
Diagnostic Process and Testing
Diagnosing severe emphysema requires a comprehensive medical evaluation and several specific tests:
Physical Examination and Medical History
Doctors begin with a thorough physical examination and detailed review of medical history, including smoking history and exposure to environmental pollutants.
Diagnostic Tests
- Pulmonary Function Tests (PFTs)
- Chest X-rays
- CT scans
- Arterial blood gas analysis
- Exercise tolerance tests
Treatment Approaches for Severe Emphysema
Medications
Several medication options can help manage symptoms and improve breathing:
- Bronchodilators
- Inhaled corticosteroids
- Antibiotics for infections
- Combination therapies
Pulmonary Rehabilitation
Comprehensive pulmonary rehabilitation programs include:
- Breathing exercises
- Physical conditioning
- Nutritional counseling
- Energy conservation techniques
- Education about the disease
Advanced Treatment Options
Surgical Interventions
For some patients with severe emphysema, surgical options may be considered:
- Lung volume reduction surgery (LVRS)
- Bullectomy
- Lung transplantation
Bronchoscopic Procedures
Minimally invasive procedures such as valve placement or coil implantation may help reduce hyperinflation and improve breathing in selected patients.
Lifestyle Management and Prevention
Managing severe emphysema requires significant lifestyle modifications:
- Smoking cessation support
- Regular exercise within limitations
- Proper nutrition
- Stress management
- Avoiding environmental irritants
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common symptoms of severe emphysema that affect daily life?
Common symptoms include severe shortness of breath, chronic cough, wheezing, and difficulty performing daily activities. Patients often experience fatigue, weight loss, and may require supplemental oxygen for routine tasks.
How is severe emphysema diagnosed and what tests are used?
Diagnosis involves pulmonary function tests, chest imaging (X-rays and CT scans), and arterial blood gas analysis. Doctors also conduct physical examinations and review medical history to assess the severity of the condition.
What treatment options are available for managing advanced emphysema?
Treatment options include medications (bronchodilators and corticosteroids), pulmonary rehabilitation, oxygen therapy, and in some cases, surgical interventions. The treatment plan is typically customized based on symptom severity and overall health status.
Can lung surgery or lung transplantation improve quality of life for severe emphysema patients?
Yes, surgical options like lung volume reduction surgery or lung transplantation can significantly improve quality of life in carefully selected patients. However, these procedures carry risks and require thorough evaluation to determine suitable candidates.
How can quitting smoking impact the progression and management of severe emphysema?
Quitting smoking is the most important step in managing emphysema. It can slow disease progression, improve treatment effectiveness, reduce infection risk, and enhance overall lung function and quality of life.