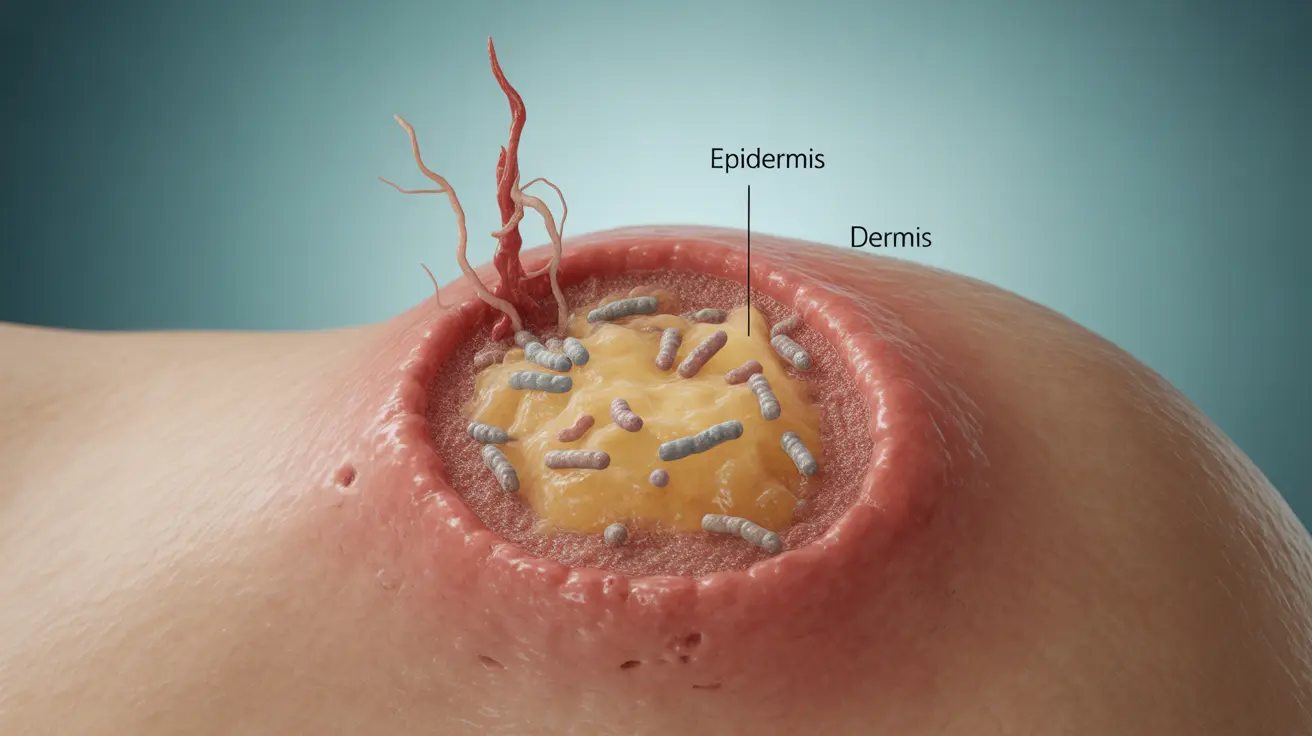
A skin abscess is a painful, swollen collection of pus that forms beneath the skin's surface. These bacterial infections can occur anywhere on the body and require proper attention to prevent complications. Understanding the signs, causes, and appropriate treatments is crucial for managing this common but potentially serious condition.
While skin abscesses can be uncomfortable and concerning, most can be effectively treated with proper medical care. This comprehensive guide will help you recognize when to seek professional help and understand the various treatment options available.
What Is a Skin Abscess?
A skin abscess develops when bacteria enter the skin through a cut, scrape, or hair follicle, causing an infection that leads to pus formation. The body's immune response creates a barrier around the infection, resulting in a painful, raised area filled with bacteria, white blood cells, and dead tissue.
Signs and Symptoms to Watch For
Recognizing the symptoms of a skin abscess early can help ensure proper treatment and prevent complications. Common signs include:
- A tender, warm, red bump or mass under the skin
- Swelling and inflammation around the affected area
- Pain that increases over time
- A visible collection of pus under the skin
- Fever in some cases
- Skin that feels hot to the touch
Risk Factors and Causes
Several factors can increase your risk of developing a skin abscess:
- Compromised immune system
- Poor hygiene
- Certain skin conditions
- Close contact with someone who has a skin infection
- Diabetes
- Obesity
When to Seek Medical Attention
While some minor abscesses may heal on their own, certain situations require immediate medical evaluation:
- Abscesses larger than 1 inch in diameter
- Those located on the face or sensitive areas
- Symptoms of systemic infection (fever, chills)
- Rapid growth or spreading redness
- Severe pain
- Failure to improve with home treatment
Treatment Options
Professional Medical Treatment
Healthcare providers typically treat significant skin abscesses through:
- Incision and drainage (I&D) procedure
- Prescribed antibiotics when necessary
- Culture testing to identify the specific bacteria
- Regular monitoring and follow-up care
Home Care Measures
For minor abscesses, these supportive measures may help:
- Warm compress application
- Keeping the area clean and covered
- Proper hand hygiene
- Over-the-counter pain relievers
- Regular monitoring for signs of worsening
Prevention Strategies
To reduce your risk of developing skin abscesses:
- Practice good personal hygiene
- Clean and protect any skin injuries
- Avoid sharing personal items
- Maintain a healthy immune system
- Seek prompt treatment for skin infections
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common symptoms and causes of a skin abscess?
Common symptoms include a painful, swollen area filled with pus, redness, warmth, and tenderness. Causes typically involve bacterial infections entering through breaks in the skin, often Staphylococcus aureus bacteria. Risk factors include poor hygiene, weakened immune system, and certain medical conditions.
How is a skin abscess diagnosed and when should I see a doctor?
Doctors diagnose skin abscesses through physical examination and sometimes culture testing. Seek medical attention if the abscess is large (over 1 inch), on your face, accompanied by fever, or shows signs of spreading infection.
What treatments are effective for skin abscesses, and can they be treated at home?
Professional treatment usually involves incision and drainage, sometimes with antibiotics. Minor abscesses may respond to home care with warm compresses and proper hygiene, but medical evaluation is often necessary to ensure appropriate treatment.
Why should I avoid squeezing or popping a skin abscess myself?
Self-drainage can spread the infection, push it deeper into the skin, cause scarring, and lead to more serious complications. Professional medical treatment ensures safe and complete drainage while preventing infection spread.
How can I prevent skin abscesses and reduce the risk of infection?
Prevention includes maintaining good hygiene, promptly cleaning and covering wounds, avoiding shared personal items, and supporting immune health through proper nutrition and lifestyle habits. Regular handwashing and proper skin care are essential preventive measures.