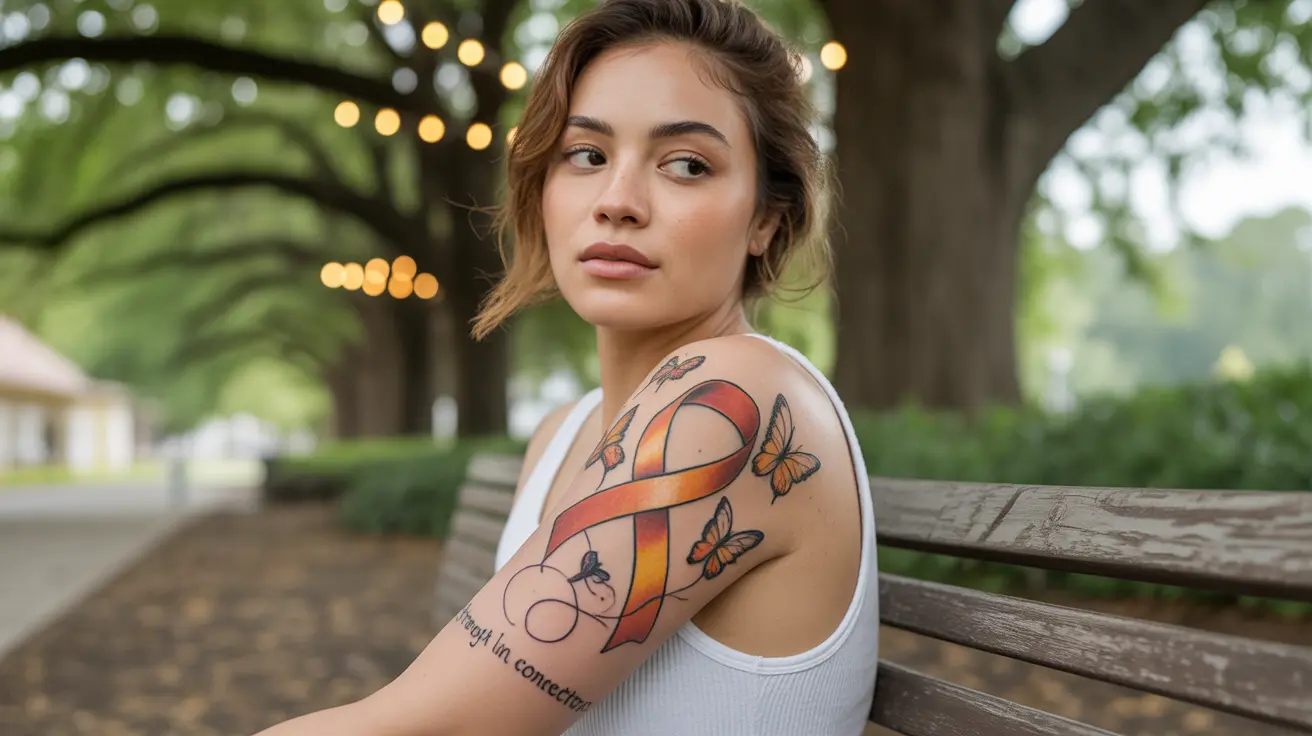GetLabTest News
Symptom Analysis
Interpreting Test Results
Diseases & Symptoms
Health Queries Answered
All
Latest
Understanding Frontotemporal Dementia: Symptoms, Treatment, and Support
Learn about Wendy Williams dementia, its symptoms, and effective treatment strategies for frontotemporal dementia and primary progressive aphasia.
Explore the differences between allergy blood tests vs skin tests to make informed health decisions.
Interpreting Test Results
min read
Discover how GERD affects fatigue and tiredness. Learn effective strategies to manage acid reflux and improve energy levels.
Diseases & Symptoms
min read

Explore hemophilia complications and effective strategies for prevention and management. Stay informed.
Diseases & Symptoms
min read
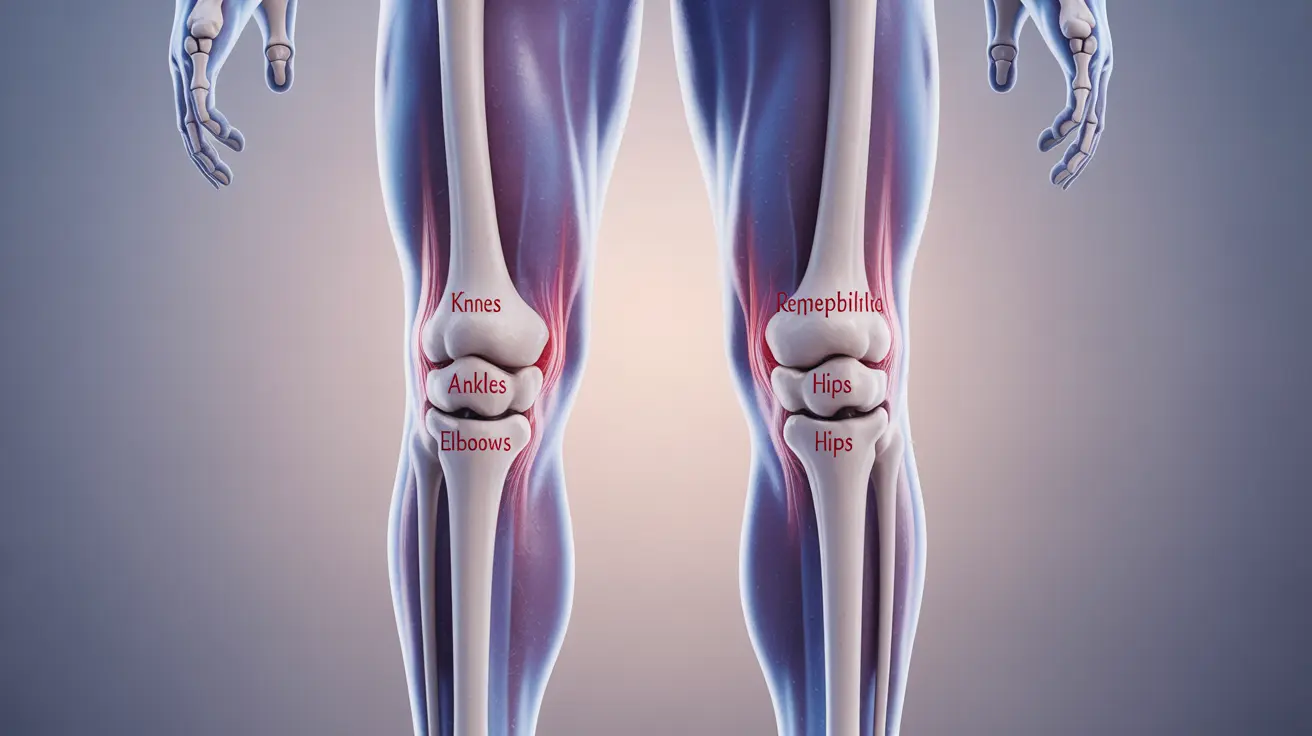
Explore inspiring multiple sclerosis tattoo ideas representing hope and resilience. Discover personal stories and community impacts.
Diseases & Symptoms
min read