GetLabTest News
Symptom Analysis
Interpreting Test Results
Diseases & Symptoms
Health Queries Answered
All
Latest
How to Be a Better Person and Be Happy: A Complete Guide to Personal Growth
Explore essential strategies on how to be a better person and be happy through mindfulness, empathy, and personal growth techniques.

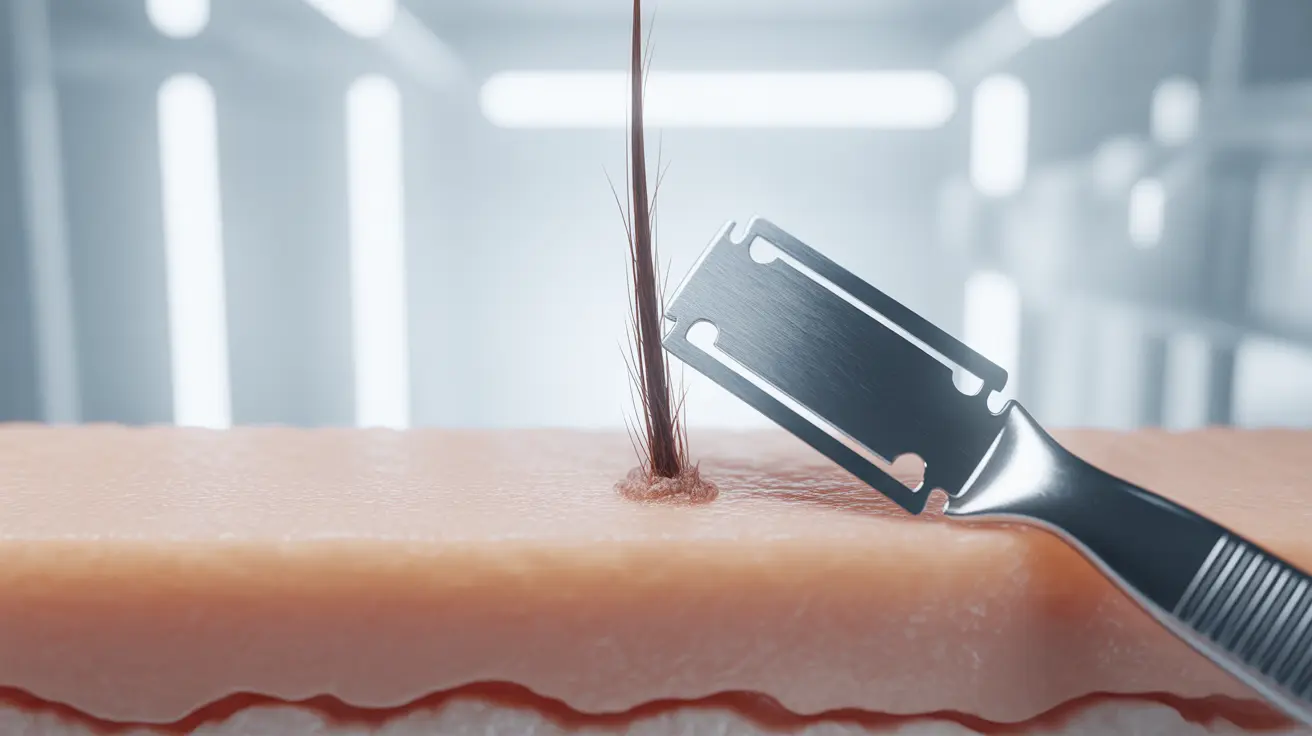
Discover the truth about shaving and hair growth. Learn why does shaving make hair thicker is a myth backed by science.
Health Queries Answered
min read
Explore the effectiveness of magnetic bracelets for pain relief. Learn the science and whether they actually work. Get informed now!
Health Queries Answered
min read

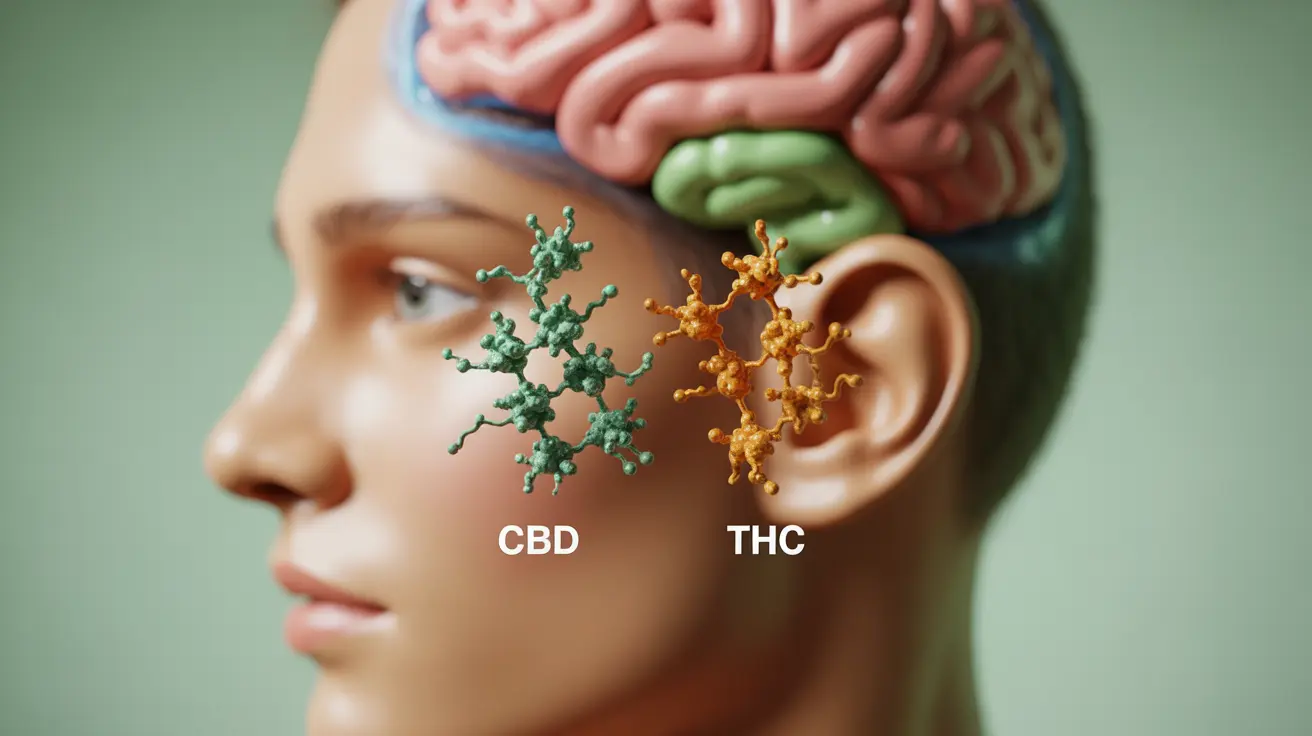
Discover if CBD gets you high and understand its effects on health. Learn about CBD's safety profile and therapeutic potential.
Health Queries Answered
min read
Explore anger management therapy techniques to improve emotional control and relationships. Learn to manage anger constructively.
Health Queries Answered
min read

