GetLabTest News
Symptom Analysis
Interpreting Test Results
Diseases & Symptoms
Health Queries Answered
All
Latest
How to Be a Better Person and Be Happy: A Complete Guide to Personal Growth
Explore essential strategies on how to be a better person and be happy through mindfulness, empathy, and personal growth techniques.

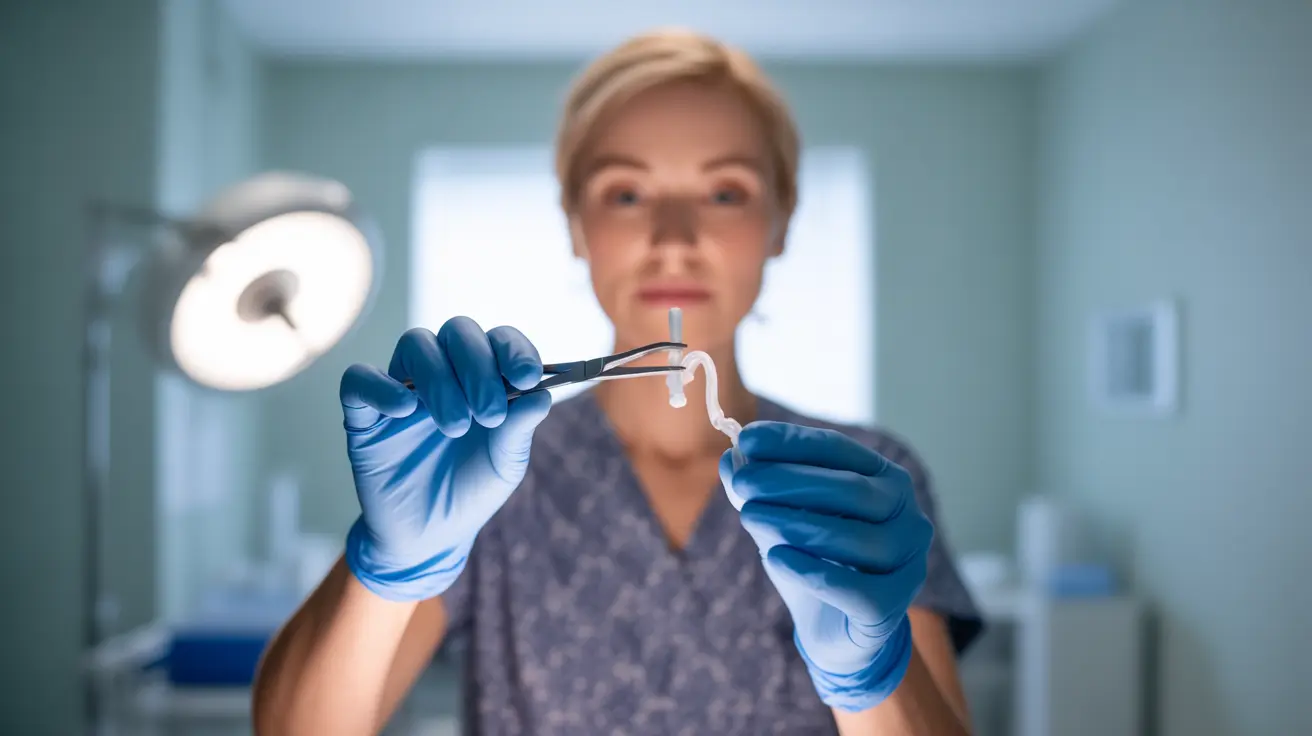
Discover the risks and important considerations of how to remove an IUD at home. Learn about safety and when to seek professional help.
Health Queries Answered
min read
Explore if pure diffusers are safe for aromatherapy. Compare risks of diffusers versus vaping essential oils for better respiratory health.
Health Queries Answered
min read

Discover the benefits, risks, and safety of baking soda deodorant. Learn if it's the right choice for your skin type.
Health Queries Answered
min read

Discover effective methods on how to thaw chicken fast while ensuring food safety. Quick tips for your kitchen included.
Health Queries Answered
min read

