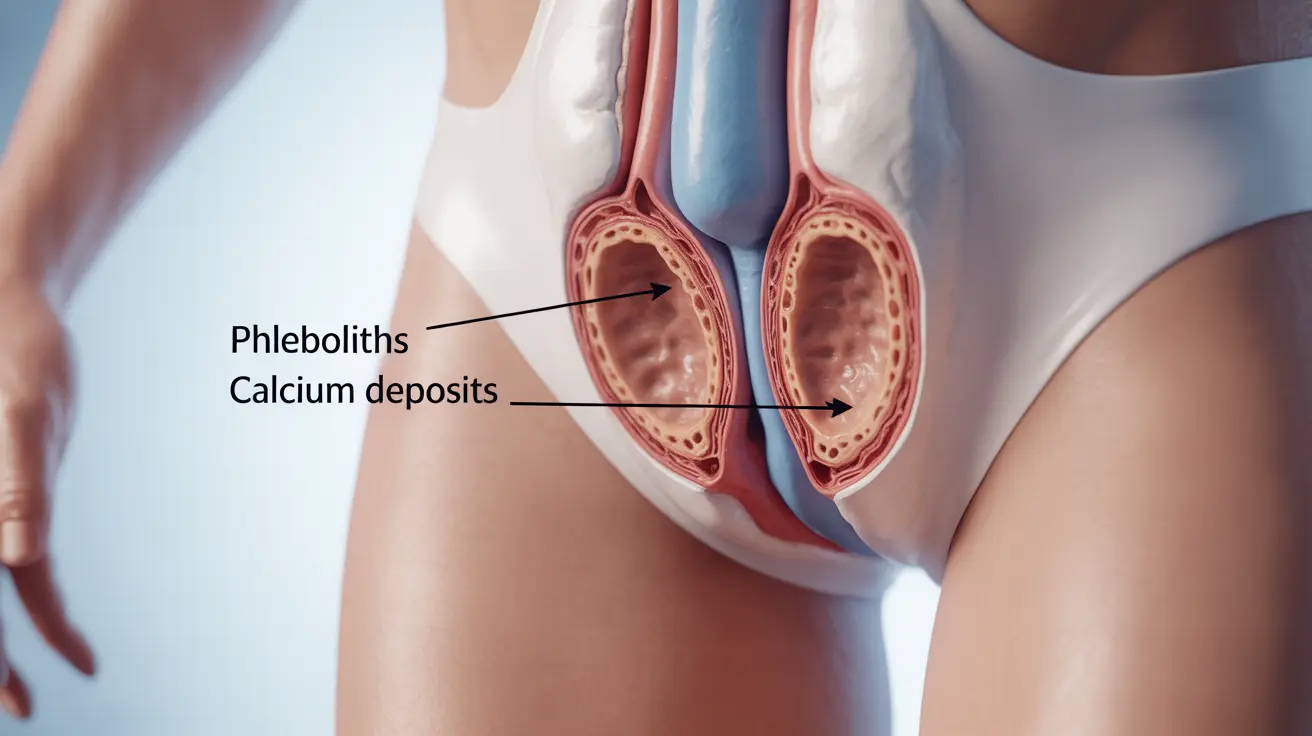
Phleboliths are small, calcified deposits that develop within veins, most commonly occurring in the pelvic region. These tiny calcium formations develop over time when blood flow becomes sluggish or disrupted in small veins, leading to mineral deposits that eventually harden. While often discovered incidentally during imaging studies, understanding phleboliths is important for both healthcare providers and patients.
These vascular calcifications are relatively common, especially in adults over 40, and their presence can sometimes indicate underlying venous conditions that may require attention. Let's explore the key aspects of phleboliths, from their formation to their potential health implications.
How Phleboliths Form
The formation of phleboliths typically occurs through a gradual process involving several stages:
- Initial blood clot formation in small veins
- Gradual calcium deposit accumulation
- Progressive hardening of the deposits
- Formation of round or oval-shaped calcifications
This process most commonly affects the pelvic veins but can occur in other parts of the body where blood flow becomes slow or irregular. The likelihood of developing phleboliths increases with age and certain risk factors.
Common Locations and Risk Factors
Phleboliths most frequently develop in specific areas of the body:
- Pelvic region
- Lower abdomen
- Vertebral column area
- Small veins near the pelvis
Several factors can increase the likelihood of developing phleboliths:
- Advanced age
- Prolonged periods of inactivity
- History of blood clots
- Venous insufficiency
- Pregnancy and childbirth history
Symptoms and Clinical Significance
Many people with phleboliths experience no symptoms at all. However, when symptoms do occur, they may include:
- Mild localized pain
- Discomfort in the pelvic region
- Pressure sensations
- Occasional cramping
While phleboliths themselves are generally harmless, their presence might indicate underlying venous conditions that warrant medical attention.
Diagnosis and Medical Assessment
Healthcare providers typically discover phleboliths through various imaging techniques:
- X-rays
- CT scans
- MRI studies
- Ultrasound examinations
Medical professionals must carefully distinguish phleboliths from other calcifications, such as kidney stones or gallstones, to ensure appropriate treatment planning.
Treatment Approaches
Most phleboliths don't require specific treatment, but management may focus on:
- Addressing underlying venous conditions
- Improving circulation
- Managing any associated symptoms
- Preventing new formations
When treatment is necessary, it typically targets the underlying vascular issues rather than the phleboliths themselves.
Prevention and Management Strategies
While not all phleboliths can be prevented, certain measures may help reduce their formation:
- Regular physical activity
- Maintaining healthy circulation
- Proper hydration
- Managing underlying vascular conditions
- Regular medical check-ups when necessary
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are phleboliths and how do they form in the veins? Phleboliths are calcified deposits that form within veins when blood flow becomes sluggish, leading to mineral accumulation and hardening. They typically develop from small blood clots that gradually collect calcium and other minerals over time.
2. What symptoms might indicate the presence of phleboliths, especially in the pelvic area? Most phleboliths are asymptomatic, but some people may experience mild localized pain, pelvic discomfort, or pressure sensations. However, these symptoms often relate more to underlying venous conditions than the phleboliths themselves.
3. How are phleboliths diagnosed and distinguished from kidney stones or other calcifications? Phleboliths are typically diagnosed through imaging studies like CT scans, X-rays, or MRIs. Medical professionals can distinguish them from other calcifications based on their characteristic round or oval shape, location, and pattern of distribution.
4. When do phleboliths require treatment and what are the common treatment options? Most phleboliths don't require specific treatment unless they cause symptoms or indicate underlying venous problems. Treatment typically focuses on managing any associated vascular conditions and improving overall circulation.
5. Can phleboliths cause complications or indicate underlying vein problems like varicose veins or venous malformations? While phleboliths themselves rarely cause complications, they can be markers of underlying venous conditions such as venous insufficiency or malformations. Their presence might warrant further evaluation of the vascular system, especially if accompanied by symptoms.