GetLabTest News
Symptom Analysis
Interpreting Test Results
Diseases & Symptoms
Health Queries Answered
All
Latest
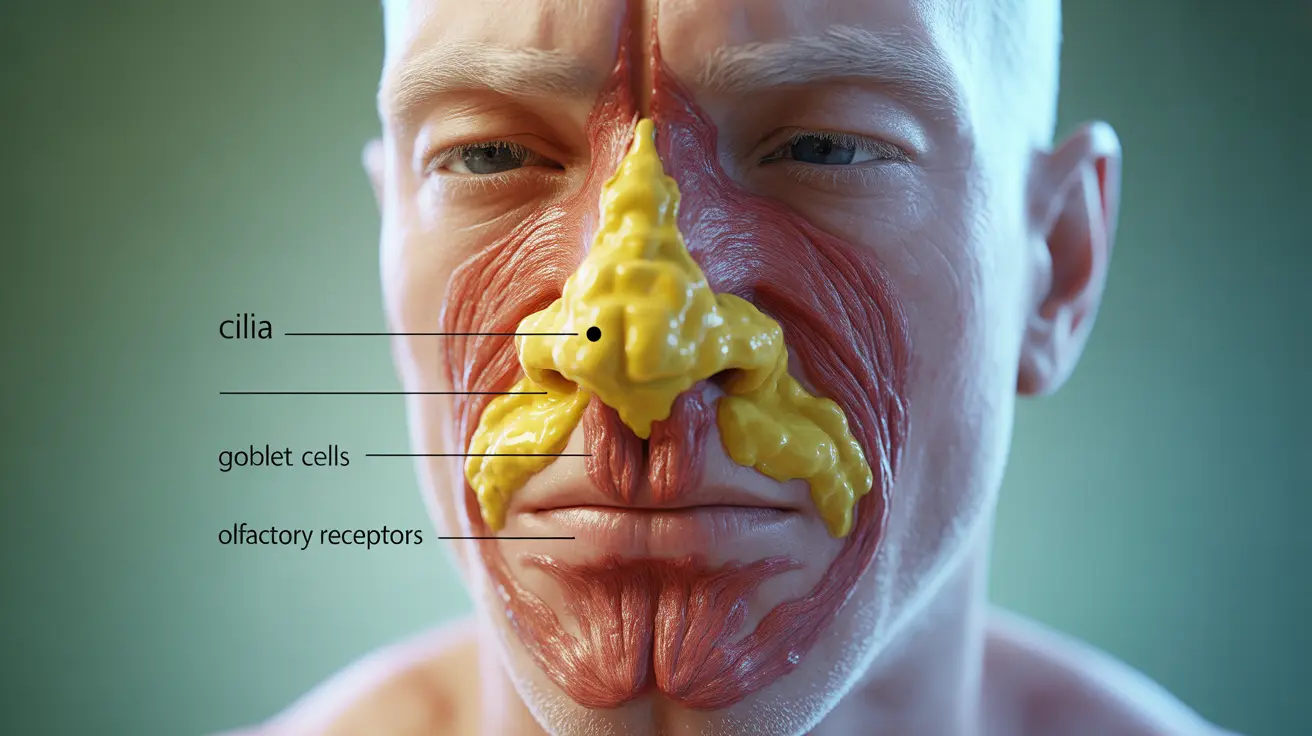
Eating Boogers: Health Risks, Scientific Facts, and Breaking the Habit
Discover the health risks of eating boogers and ways to break the habit. Learn the science behind this common behavior and its implications.
Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) is a crucial marker for assessing thyroid function and diagnosing thyroid disorders. A TSH blood test measures the amount of this hormone produced by the pituitary gland, which regulates the thyroid. High TSH levels indicate hypothyroidism, where the thyroid is underactive and not producing enough hormones. Conversely, low TSH levels suggest hyperthyroidism, an overactive thyroid producing too much hormone. TSH testing is essential for monitoring thyroid conditions and determining the appropriate treatment, which may involve medications to regulate hormone levels, depending on whether thyroid function is too high or too low.
Health Queries Answered
min read

A Full Blood Count (FBC) is an essential test for detecting anemia. It measures various components of the blood, including red blood cells (RBCs), hemoglobin, and hematocrit levels. These elements are crucial in assessing the body's ability to carry oxygen. When levels fall below the normal range, it can indicate anemia, a condition characterized by fatigue, weakness, and pale skin. Interpreting FBC results allows healthcare providers to determine the severity and type of anemia, helping to guide treatment. Regular FBC testing is critical for those at risk of anemia, such as people with chronic illnesses or nutritional deficiencies.
Health Queries Answered
min read

Serum ALT (alanine aminotransferase) levels are measured in a blood test to assess liver health. ALT is an enzyme found mainly in the liver, and its levels rise when liver cells are damaged or inflamed. Normal ALT levels typically range from 7 to 56 units per liter (U/L), although the range may vary slightly between labs. Elevated ALT levels can indicate liver conditions such as hepatitis, fatty liver disease, or cirrhosis, while significantly low levels are rare but may point to nutritional deficiencies. Monitoring ALT helps detect liver damage early, aiding timely treatment.
Health Queries Answered
min read

Serum creatinine is a blood test that measures the amount of creatinine, a waste product produced by muscles, in your bloodstream. This test helps assess how well your kidneys are filtering waste from your blood. Normal levels vary depending on age, sex, and muscle mass. Elevated creatinine levels may indicate impaired kidney function or kidney disease. Conversely, lower-than-normal levels may be seen in individuals with low muscle mass or certain chronic conditions. Regular monitoring of serum creatinine can help detect early signs of kidney dysfunction, making it a vital tool for kidney health assessment.
Health Queries Answered
min read
