GetLabTest News
Symptom Analysis
Interpreting Test Results
Diseases & Symptoms
Health Queries Answered
All
Latest
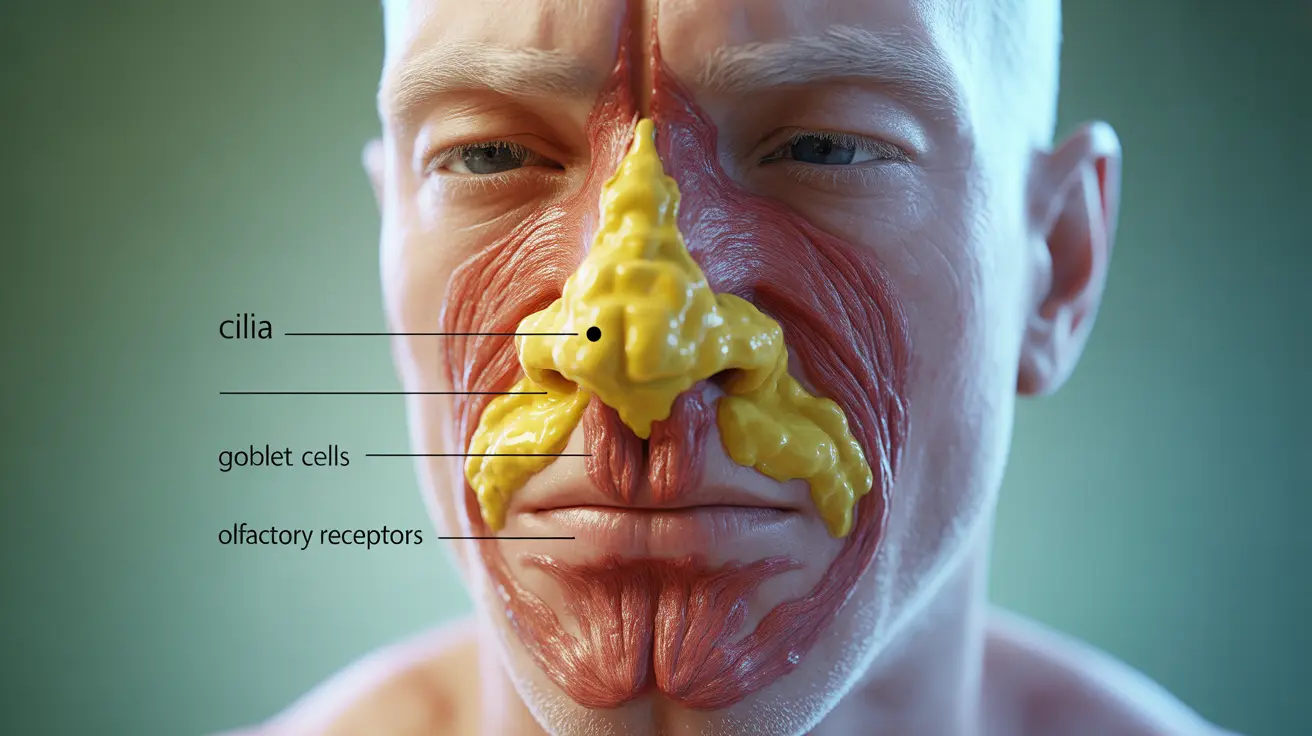
Eating Boogers: Health Risks, Scientific Facts, and Breaking the Habit
Discover the health risks of eating boogers and ways to break the habit. Learn the science behind this common behavior and its implications.
The Albumin to Creatinine Ratio (ACR) test measures the amount of albumin, a protein, in your urine relative to creatinine. This test is crucial for diabetics because it helps detect early signs of kidney damage. High levels of albumin in the urine (a condition called microalbuminuria) can indicate that the kidneys are not filtering blood effectively, which is a common complication of diabetes. By catching kidney issues early, the ACR test allows for timely intervention to prevent further kidney damage, making it an essential part of diabetes management.
Health Queries Answered
min read

A Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone (TSH) blood test measures the levels of TSH, which regulates the production of thyroid hormones. It helps assess thyroid function and can indicate either an underactive thyroid (hypothyroidism) or an overactive thyroid (hyperthyroidism). High TSH levels typically suggest hypothyroidism, while low TSH levels point toward hyperthyroidism. The TSH test is crucial for diagnosing thyroid disorders, guiding treatment, and monitoring the effects of thyroid medications. It’s often recommended if a person has symptoms like fatigue, weight changes, or irregular heartbeats, which could indicate thyroid dysfunction.
Health Queries Answered
min read

HbA1c measures your average blood sugar levels over the past 2-3 months, making it a key marker for diabetes management and overall blood sugar control. Diet and lifestyle play a significant role in affecting HbA1c levels. Consuming a balanced diet rich in whole grains, lean proteins, and vegetables while avoiding excessive sugar and processed foods can help maintain healthy HbA1c levels. Regular physical activity, stress management, and proper sleep also contribute to keeping blood sugar levels stable. Regular testing of HbA1c helps monitor long-term glucose control, especially for those with diabetes or at risk of developing it.
Health Queries Answered
min read

Serum urea levels are a key indicator of kidney function, reflecting how well the kidneys are filtering waste from the blood. Urea is a byproduct of protein metabolism, and its concentration in the blood can reveal potential issues with kidney health. Normal serum urea levels generally range between 2.5 to 7.1 mmol/L, although these values may vary slightly depending on the laboratory. Elevated urea levels could indicate impaired kidney function, dehydration, or high protein intake, while low levels may suggest liver disease or malnutrition. A urea test is commonly paired with creatinine levels for a comprehensive kidney function assessment.
Health Queries Answered
min read
