GetLabTest News
Symptom Analysis
Interpreting Test Results
Diseases & Symptoms
Health Queries Answered
All
Latest
How to Be a Better Person and Be Happy: A Complete Guide to Personal Growth
Explore essential strategies on how to be a better person and be happy through mindfulness, empathy, and personal growth techniques.

Discover whether basmati rice is healthy and learn about its nutritional benefits, especially brown vs. white basmati rice.
Health Queries Answered
min read

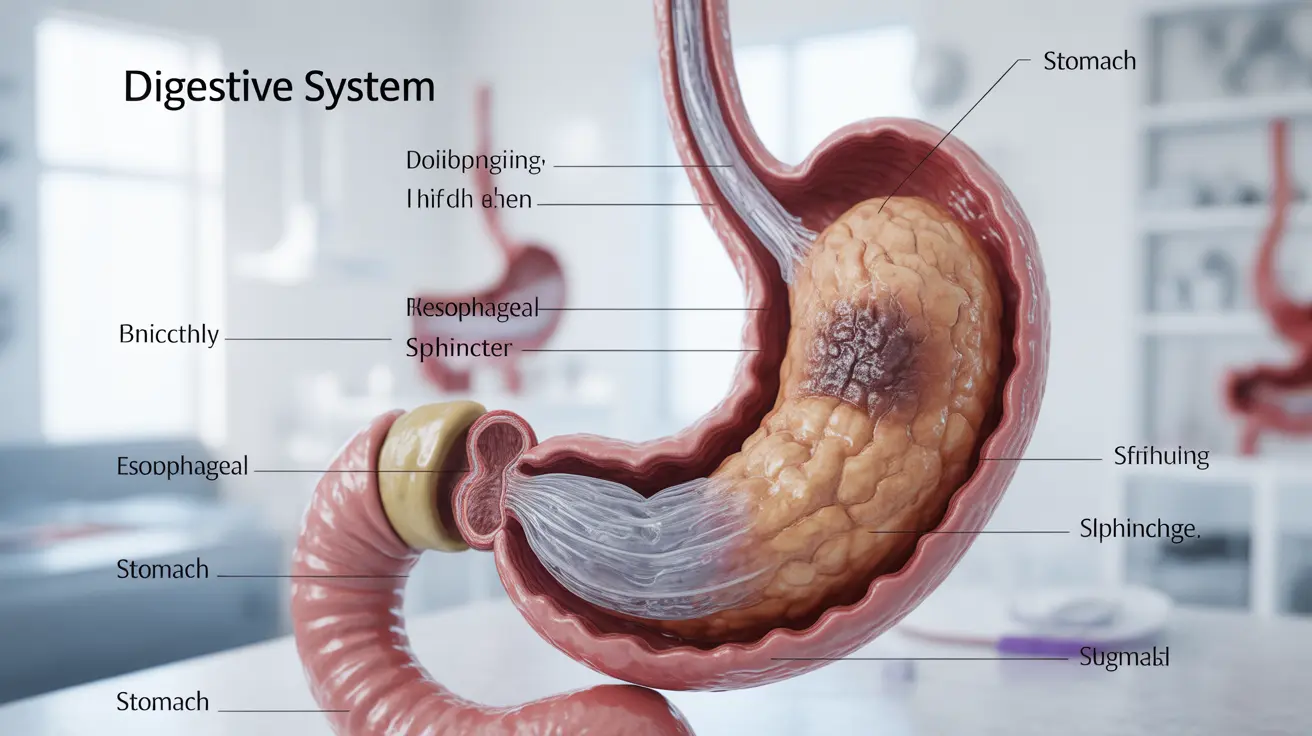
Discover how to stop stomach pain from smoking with practical tips and treatment strategies to support your digestive health effectively.
Health Queries Answered
min read
Discover the truth about whether lime lightens skin, its risks, and safer alternatives for achieving a brighter complexion.
Health Queries Answered
min read
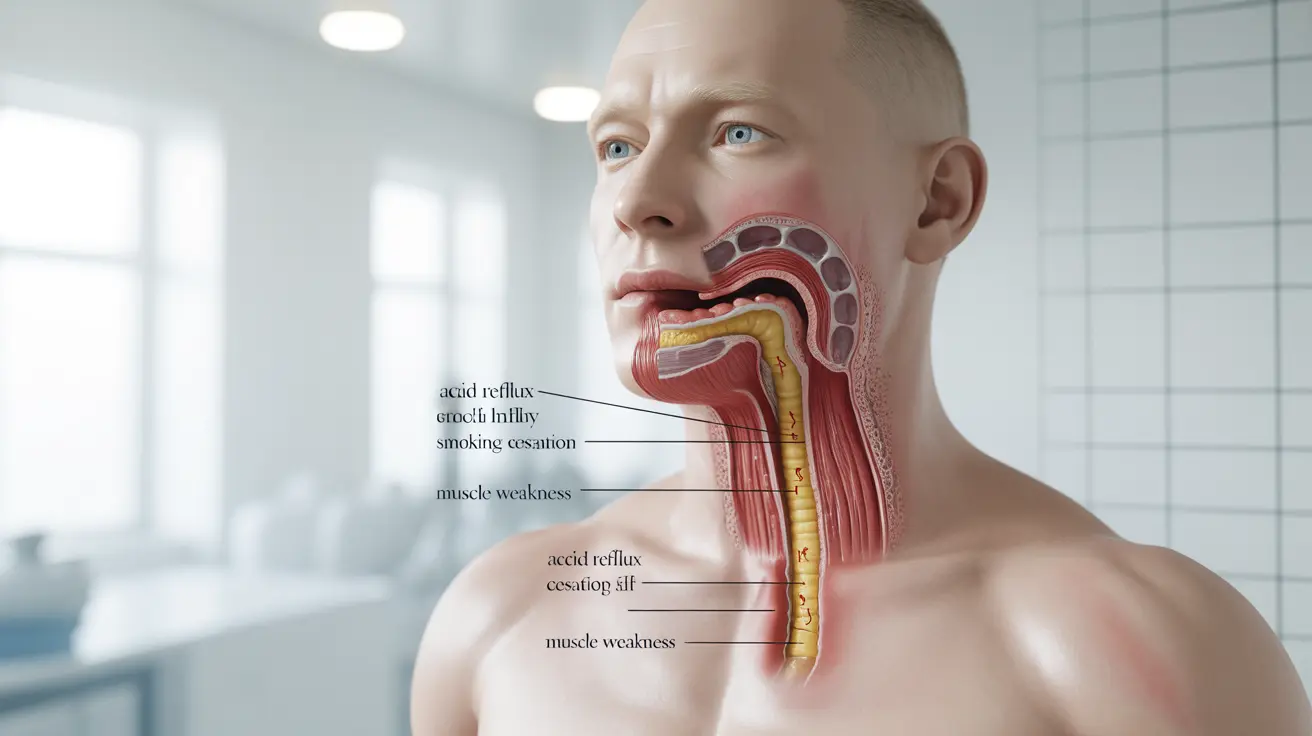
Discover if quitting smoking can cause acid reflux and learn effective management strategies during this transition for better digestive health.
Health Queries Answered
min read